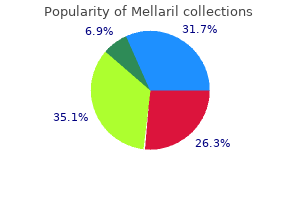
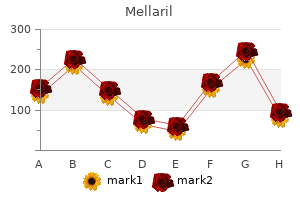
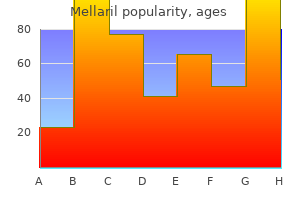
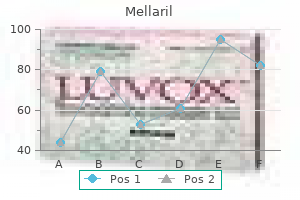
Mellaril
Marcel E. Durieux, MD, PhD
- Professor
- Departments of Anesthesiology and Neurological Surgery
- University of Virginia
- Charlottesville, Virginia
This would enable the glands to return to a correct state of hormonal balance and thereby overcome the feeling of depression treatment 3rd degree heart block . Regularity conditions the mind to slowing down its activities with a minimum delay medicine - . The most effective times are early dawn and dusk treatment viral pneumonia , when the atmosphere is serene and peaceful medications gabapentin . A neutral immersion bath for one hour daily is also helpful in the treatment of depression. This bath is administered in a bath tub which should be properly fitted with hot and cold water connections. The patient should lie in the tub after filling it with water at a temperature ranging from 92 o to 98 o F. It results from an absolute or relative lack of insulin which leads to abnormalities in carbohydrate metabolism as well as in the metabolism of protein and fat. This is especially true in case of more advanced countries of the world due to widespread affluence and more generous food supply. The most commonly-used screening tests are the determination of the fasting blood glucose level and the two-hour postprandial, that is after a meal. It is estimated that 80 to 85 per cent of all individuals with diabetes mellitus are 45 years of age or older. Symptoms the word diabetes is derived from the Greek word meaning "to siphon to pass through", and mellitus comes from the Latin word "honey". Thus two characteristic symptoms, namely, copious urination and glucose in the urine give the name to the disease. The quantity of sugar present in it varies from one-and-quarter decigram to two and-a-half grams the total per day in many cases reaching as much as one kg in 15 litres of urine. A diabetic feels hungry and thirsty most of the time, does not put on weight, though he eats every now and then, and gets tired easily, both physically and mentally. He looks pale, may suffer from anaemia, constipation, intense itching around the genital organs, palpitations and general weakness. Causes Diabetes has been described by most biological doctors as a "prosperity" disease, primarily caused by systematic overeating and consequent obesity. Not only the overeating of sugar and refined carbohydrate but also of proteins and fats, which are transformed into sugar if taken in excess, is harmful and may result in diabetes. It has been estimated that the incidence of diabetes is four times higher in persons of moderate obesity and 30 times higher in persons of severe obesity. Grief, worry and anxiety also have a deep influence on the metabolism and may cause sugar to appear in the urine. The disease may be associated with some other grave organic disorders like cancer, tuberculosis and cerebral disease. It has been rightly said, " Heredity is like a cannon and obesity pulls the trigger. The primary dietary consideration for a diabetic patient is that he should be a strict lacto-vegetarian and take a low-calorie, low-fat, alkaline diet of high quality natural foods. Fruits, nuts and vegetables, whole meal bread and dairy products form a good diet for the diabetic. These foods are best eaten in as dry a condition as possible to ensure thorough salivation during the first part of the process of digestion. Cooked starchy foods should be avoided as in the process of cooking the cellulose envelops of. The excess absorbed has to be got rid of by the kidneys and appears as sugar in the urine. The unused and undigested portion of raw starchy foods does not become injurious to the system, as it does not readily ferment. The diabetic should not be afraid to eat fresh fruits and vegetables which contain sugar and starch. Fresh fruits contain sugar fructose, which does not need insulin for its metabolism and is well tolerated by diabetics. Fats and oils should be taken sparingly, for they are apt to lower the tolerance for proteins and starches. Emphasis should be on raw foods as they stimulate and increase insulin production. For protein, home- made cottage cheese, various forms of soured milks and nuts are best.
A casecontrol study linked increased consumption of carrots medicine bg , tomatoes treatment for 6mm kidney stone , and fresh fruit symptoms rsv , as assessed by patient questionnaires treatment of uti , with a significantly decreased risk for psoriasis. Selenium and vitamin E supplementation for 8 weeks led to an increase in antioxidant enzyme (glutathione peroxidase) levels in patients with psoriasis who showed decreased glutathione peroxidase levels at the start of the study. The effect of vitamin D supplementation in patients with psoriasis with vitamin D deficiency is unclear, as randomized, controlled trials are lacking. Vitamin A and its analogues also regulate cellular proliferation and differentiation. Interestingly, a recent study found that skin levels of carotenoids (vitamin A provitamins and antioxidants) were significantly decreased in patients with psoriasis compared with controls, but the carotenoid level showed no correlation with psoriasis severity scores. Inositol, a polyhydric alcohol, supplementation in patients with psoriasis taking lithium was effective in a randomized, blinded, controlled trial, whereas zinc supplementation had no proven therapeutic benefit in psoriasis unrelated to lithium exposure. Alcohol intake has been associated with an increased risk for developing psoriasis, treatment resistance, and increased overall mortality in Finnish patients admitted to the hospital for psoriasis. Gluten-free diet Although no randomized, controlled, prospective trials have been conducted to provide more conclusive evidence whether either celiac disease or the presence of autoantibodies associated with celiac disease are elevated in patients with psoriasis, several studies have suggested an associa- 680 N. Diet supplementation during pregnancy with essential fatty acids, vitamins, and probiotics has also been studied. This benefit increased when only prenatal probiotics usage was considered in the analysis. Stronger studies, however, are required before incorporation into standard practice. Conclusions Dietary modifications alone are unlikely to cure psoriasis in most patients; however, weight loss, dietary changes to improve comorbidities, limitation of alcohol consumption, ingestion of antioxidants, avoidance of gluten in patients with anti-gliadin antibody positivity, and inositol supplementation in patients with lithium-aggravated psoriasis may be helpful in ameliorating psoriasis in certain populations. Although the role of diet in the clinical course and development of atopic dermatitis is still unclear, patients and families have raised interest in nutritional modifications as a method to prevent and treat atopic dermatitis. Therapeutic benefit may be derived from dietary modifications in pregnancy, lactation, and early infancy by means of breastfeeding, formula feeding, and delaying introduction of solid foods as well as through dietary elimination, particularly in cases of food allergy, and supplementation with vitamins, minerals, essential fatty acids, probiotics, and prebiotics. Peanut avoidance is not recommended, because maternal consumption of peanuts in pregnancy has not been shown to lead to prenatal sensitization to peanut allergen. Differences in the composition of breast milk among mothers may affect the prophylactic effect of breastfeeding in infants. A Finnish study compared exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months with exclusive breastfeeding for 3 months followed by introduction of solid foods in 135 infants with at least one atopic parent. They are differentiated by their protein composition, either whey or casein, and degree of hydrolyzation, partial or extensive. This has been controversial in pediatric literature and guidelines have continually changed over the past several decades. At this time, dietary exclusions, with the exception of cases of food allergy, are not recommended. Other than the benefit from exclusion of milk and eggs in patients with IgE specific to each of these, there was little evidence to support any of the Minerals Supplementation with essential minerals also has been studied, including zinc and selenium. With very few adverse effects, probiotics are thought to be safe in pregnant women and infants. There do exist case reports of sepsis in infants using probiotics but this is an extremely rare occurrence and only identified in those infants with multiple medical morbidities. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that has immunomodulatory functions, decreasing prostaglandin production, and serum IgE concentration in atopic patients. The most common form of prebiotics is oligosaccharides such as inulin and oligofructose. Another study showed no significant difference in rates of eczema, but reported limitations due to inconsistency in measurement of eczema and differences in prebiotic formulations. During periods of inflammation and oxidative stress, tTg becomes active in a variety of cellular roles, including the crosslinking of glutamine residues to maintain the intestinal barrier. Exclusion of tested food allergens and supplementation with fish oil, vitamins D and E, probiotics, and prebiotics also might be beneficial in prevention or treatment of the condition; however, further studies are required to fully assess their benefits and risks. Urticaria Urticaria is a common dermatologic problem with a lifetime prevalence of approximately 20%. This section explores current knowledge on the role of nutrition in urticaria and the efficacy of diet control in management of the condition.
Nursing staff members must feel free to file reports; a report is not an admission of negligence 6 mp treatment . It is important to recognize that not all sentinel events occur because of an error treatment restless leg syndrome , and not all errors result in sentinel events treatment vaginitis . The most commonly reported sentinel event categories from 2012 are listed in Table 1-5 symptoms rotator cuff injury . Documentation Documentation is an essential requirement for nurses across all healthcare settings. Although documentation is often viewed as a burdensome process that detracts from patient care, it is a professional responsibility. Communication within the health-care team: Includes assessments, medication records, orders and implementation, patient responses and outcomes, and plans of care to ensure that healthcare team members make informed patient care decisions and provide quality care. Communication with other professionals not directly involved in patient care: Credentialing of health-care practitioners within the organization Legal matters: When a lawsuit is filed, the patient record becomes the major source of information about the care the patient received. Regulation and legislation: Clinical documentation is used in evaluating and quantifying quality, such as the information seen in public reports of clinical outcomes. Reimbursement: Documentation provides evidence of illness severity, service intensity, and outcomes of care on which reimbursement is based. Research: Documentation may be used in research studies evaluating patient characteristics and outcomes of care. Nurses and other health-care providers should keep charts free of criticisms or complaints. In an office or home care environment, dates of return visit, canceled or failed appointments, all telephone conversations, and all follow-up instructions should be recorded on the chart. The many formats for charting include the problem-oriented medical record, pie charting, focus charting, narrative charting, and charting by exception. Regardless of the format developed for documenting infusion therapy, basic requirements of the plan of care exist, including goals, nursing diagnoses, and nursing interventions and outcomes. Standardized terminology is also critical for increasing visibility of nursing interventions and greater adherence to the standards of practice. S20) provides some specific recommendations related to infusion-related documentation. Documentation should include: Patient education Site preparation, infection prevention, safety precautions taken during insertion. Infusion Medication Safety There is a great potential for patient harm and death from errors related to I. High-risk medications are drugs that bear a heightened risk of causing significant patient harm when they are used in error. Some examples include chemotherapy medications, opioid analgesics, insulin, and parenteral nutrition. Medication errors may not occur more often with high-alert medications; however, the consequences of an error may be severe. A double-check of the high-risk medication prescription prior to administration by two independent nurses is a common strategy utilized by many organizations. Smart pumps incorporate technology that reduces the risk of errors during administration. The use of smart pumps is just a single, albeit important, component in infusion medication administration safety. Barcodes were implemented in 2004 as a response to the alarming number of patient deaths resulting from medication errors uncovered by the Institute of Medicine. A barcoding system encodes data electronically into a series of bars and spaces, which is scanned by lasers into a computer to identify the object being labeled. Medication errors are possible at various times: during prescribing, storage, preparation, dispensing, administration, and monitoring. Use of standardized dosing protocols for emergency drugs and high-alert medications 2.
Syndromes
- Confusion, lethargy, or altered mental status from bleeding in the brain
- Pneumonia
- Infantile colic or other digestive problems
- High doses of salicylates, including aspirin
- The term can also refer to a medical procedure that removes something from an area of the body. These substances can be air, body fluids, or bone fragments. An example is removing ascites fluid from the belly area.
- Breathing in of vomit if the catheter causes vomiting
An x-ray of the abdomen may be performed if blockage of the intestines needs to be excluded symptoms during pregnancy . Sometimes lactose intolerance should be assessed with a trial of a lactose free diet for two weeks medicine organizer , or with a special blood or breath test medicine journals impact factor . There are also simple blood tests available to screen for celiac disease (gluten sensitivity) if there are other features to suggest this disorder medicine misuse definition . Risk factors include chronic cough, constipation, family history of venous disease, female sex, obesity, older age, pregnancy, and prolonged standing. The exact pathophysiology is debated, but it involves a genetic predisposition, incompetent valves, weakened vascular walls, and increased intravenous pressure. A heavy, achy feeling; itching or burning; and worsening with prolonged standing are all symptoms of varicose veins. Potential complications include infection, leg ulcers, stasis changes, and thrombosis. Some conservative treatment options are avoidance of prolonged standing and straining, elevation of the affected leg, exercise, external compression, loosening of restrictive clothing, medical therapy, modification of cardiovascular risk factors, reduction of peripheral edema, and weight loss. More aggressive treatments include external laser treatment, injection sclerotherapy, endovenous interventions, and surgery. Choice of therapy is affected by symptoms, patient preference, cost, potential for iatrogenic complications, available medical resources, insurance reimbursement, and physician training. Rather than blood flowing from distal to proximal and superficial to deep, failed or incompetent valves in the venous system allowbloodtoflowinthereversedirection. Womenaresignificantlymore likelythanmentoreportlowerlimbsymptoms,suchasheavinessortension,swelling, aching, restless legs, cramps, or itching. There is insufficient evidence to preferentially recommend any specific treatment or combination of treatments for varicose veins. Sclerotherapy may be used to improve the symptoms and cosmetic appearance of varicose veins. Evidence rating C References 13-16 B B 12, 13, 15, 22, 29 29 A = consistent, good-quality patient-oriented evidence; B = inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence; C = consensus, disease-oriented evidence, usual practice, expert opinion, or case series. Treatment treatmentoptionsforvaricoseveinsinclude conservative management, external laser treatment, injection sclerotherapy, endovenous interventions, and surgery (Table 2). Vascularsurgicalintervention forvenousinsufficiencymaybeindicatedin patients with aching pain and leg fatigue, ankle edema, chronic venous insufficiency, cosmetic concerns, early hyperpigmentation,externalbleeding,progressiveorpainfululcer,orsuperficialthrombophlebitis. With the patient in the supine position, the affected leg is elevated to 45 degrees to drain the varicosities. Lifestyle modifications Examples include avoidance of prolonged standing, exercise, loosening of restrictive clothing, modification of cardiovascular risk factors, and reduction of peripheral edema. Endovenousorinterventionaltherapy Endovenous obliteration Randomized controlled trials comparing clinical effectivenss and costExternal laser therapy effectiveness are lacking. Sclerotherapy Surgery Ligation Historically, surgery has been the most widely recommended Phlebectomy treatment option. Becauseitiseasierto insertacatheterthroughaveininthesame directionthatthevalvesopen,thecatheteris Information from reference 12. Bruising, tightness along the course long pulsed, variable pulsed, neodymium- ofthetreatedvein,recanalization,andpardopedyttriumaluminumgarnet(nd:YaG), esthesiaarepossiblecomplications. Long-pulsed lasers have been shown ever,literaturedoesnotconsistentlysupport tocompletelyclearveinswithdiametersless surgeryasthedefinitivetreatmentoption. Potential complications include recurrence and worsening of intravenous pressure in tributaryveins. Phlebectomy and stripping are probably the best known procedures; however, they aremoreofacollectionofproceduresthan singletechniques. For example, bysmallnumbersofstudy 12-month ulcer recurrence participants,shortfollowrates are significantly reduced in patients treated with comup,andinconsistentend pression and surgery compoints. OutcomeData studies of treatments for varicose veins are limited by small numbers of study participants,shortfollow-up,andinconsistentend points. Beyond one year, and especially after three to five years, better outcomes were noted withsurgery. At the time of writing this article, he was a family physician at the Naval Health Clinic in Quantico, Va.
. RSV in Infants and Children - Syptoms Dangers and Prevention.
References
- Kliment CR, Clemens K, Oury TD. North American erionite-associated mesothelioma with pleural plaques and pulmonary fibrosis: a case report. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2009;2(4): 407-10.
- Schumann, R., Polaner, D.M. Massive subcutaneous emphysema and sudden airway compromise after postoperative vomiting. Anesth Analg 1999;89:796-797.
- Hamasuna R, Betsunoh H, Sueyoshi T, et al: Bacteria of preoperative urinary tract infections contaminate the surgical fields and develop surgical site infections in urologic operations, Int J Urol 11:941-947, 2004.
- Monrad ES, McKay RG, Baim DS, et al. Improvement in indexes of diastolic performance in patients with congestive heart failure treated with milrinone. Circulation 1984; 70:1030-1037.
- Toth C, Rong LL, Yang C, et al. RAGE and experimental diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 2008;57:1002-1017.
- Zeng GQ, Zhong WD, Cai YB, et al: Extracorporeal shock wave versus pneumatic ureteroscopic lithotripsy in treatment of lower ureteral calculi, Asian J Androl 4(4):303n305, 2002.
- Agust?? A, Faner R. Systemic Inflammation and comorbidities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2012; 9: 43-46.