Gasex
Ruby Shrestha, MD
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Abington Memorial Hospital
- Abington, Pennsylvania
In both communities gastritis diet ����������� 100 caps gasex purchase visa, inoculation has eliminated the dangers of a measles epidemic and the virus simply cannot take hold gastritis diet 80 discount gasex 100 caps. A small group of anti-vaccination activists tries to spread the contagion of doubt in the urban network and an equivalent group attempts to do the same in the suburban network gastritis diet options discount 100 caps gasex. Because the urban network does not provide any social reinforcement gastritis diet �������� buy 100 caps gasex with visa, the messages are not convincing. If the inoculation campaign succeeds as before, the antivaccination activists have not put anyone at risk but themselves (Figure 4). Success of anti-vaccine movements in urban and suburban social networks the vaccination campaign has effectively closed down the contagion pathways of spread, even if an infected person enters. Because they have less exposure to the population as a whole, they appear to be at a disadvantage compared to the activists in the urban network. However, because 133 comPlex contaGion oF douBt they share contacts within their social cluster, they can reinforce the anti-vaccination message and propagate doubt among their peers. Those peers may then become convinced that there is a real debate and that concerns about the safety of vaccination are valid. This cluster then generates a critical mass of infected individuals that can overwhelm the herd immunity serving the rest of the population, allowing every nonvaccinated person in the suburban community to contract measles (Campbell & Salathй, 2013). The complex contagion of doubt changes the dynamics of disease spread, making the clustered suburban network a far more vulnerable social setting. Measles outbreaks after anti-vaccine movements and vaccination campaigns in urban and suburban social networks. The attraction of antibiotics reflects the perceived danger of immediate infection compared to the remote individual risk of antibiotic resistance. A possible viral epidemic is a distant risk, but the perceived danger from vaccination is that it can cause immediate harm, which encourages people to recoil into a position of safety-that is, a position of inaction (Raymond, 1991). The complexity of social contagion is that it requires social reinforcement to spread. But, if the contagion of doubt spreads most effectively through clustered networks of peers, it may be possible to counteract that contagion with the same strategy. Creating networked communities-online and offline-in which social reinforcement is strategically harnessed to delegitimize the anti-vaccine arguments, is one promising approach. The strategies of complex contagions provide useful guidance for targeting places in the social network where reinforcement can either increase the credibility of the anti-vaccination movement or decrease its legitimacy (Centola, 2018). He is a series editor for Princeton University Press and the author of How Behavior Spreads: the Science of Complex Contagions. With high-profile measles outbreaks in Brooklyn, Samoa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Italy; misinformation impacting the polio eradication program in Pakistan (Bhattacharjee & Dotto, 2019); and a controversial rollout of Dengvaxia in the Philippines (Mason & Smith, 2020), vaccine-related headlines have become a feature of contemporary life. The main reasons people do not vaccinate their children when vaccines and vaccination services are otherwise available include cost; convenience; moral, philosophical, or religious objections; or lack of information about when and how to obtain vaccinations. While the conclusions have not changed substantially, some more recent trends are also included here. All of this creates the backdrop for vaccine conversations between individuals and on public forums that can be based on misleading and false conspiracy theories and rumors, whether they sit in Google search results, YouTube videos, or Facebook, Instagram, or WhatsApp messages. A study published in February 2020 demonstrated that people exposed to vaccine content on social media were more likely to be misinformed than those exposed to it on traditional media. While this survey cannot disentangle causality, the percentage of people reporting that they had seen negative information about vaccines on social media is an important data point. Scholars hope this might lead other platforms to release data so that researchers can better understand how misinformation is shared and consumed. However, much of the potentially harmful content does not sit exclusively on websites, but in Facebook posts, Instagram memes, misleading tweets, and conspiratorial YouTube videos. In April 2019, Claire Wardle (a co-author of this paper) and Alexios Mantzarlis used a new method to understand prevalence. Query results for vaccines search (different languages) Vacinaзгo em crianзas й seguro? Research by Michael Golebiewski and danah boyd (2019) on data voids explores these challenges in greater depth.
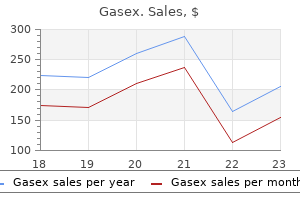
This figure includes more than $6 billion due to indirect costs (such as time lost from work) and $34 gastritis mayo clinic gasex 100 caps for sale. Influenza Influenza viruses change constantly and different strains circulate around the world every year gastritis diet 8 month cheap gasex 100 caps online. The flu vaccine is modified on the assumption of which strain will most likely be dominant throughout the season diet with gastritis cheap 100 caps gasex overnight delivery. However chronic gastritis reflux buy discount gasex 100 caps online, this prediction may not be 100 percent accurate, as has been the case with the 2007-2008 flu season. This change will take effect as soon as feasible, but no later than the 2009-2010 influenza season. FluMist is approved to prevent influenza illness due to influenza A and B viruses in healthy people aged 2 to 49 years only. In healthy adults aged 18 to 49 years, FluMist was effective in reducing severe illnesses with fever, and upper respiratory problems which may be caused by influenza infection. FluMist is not recommended for children under two years of age, children under five with recurrent wheezing or adults over 49 years of age. Initial results from the 2006-2007 influenza season indicate that children 6 to 59 months of age are under-vaccinated. Less than 30 percent of children 6 to 23 months of age were fully vaccinated during that past flu season, while less than 20 percent of children 24 to 59 months old were fully vaccinated. In 2006, among people ages 65 and older, non-Hispanic Whites were more likely to report receiving a flu shot (66. Figure 3 shows the percentage of fee-for-service Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 and older that received flu shots, by state, in 2004. Figure 4 displays the percentage of Medicare beneficiaries aged 65 and older that had ever received a pneumococcal vaccination as of 2006, by state. Total immunization rates may be higher in those areas with free or publicly-supported programs. There is a racial disparity among people ages 65 and older receiving the pneumonia shot which needs to be addressed. A number of laboratory tests are available to confirm the diagnosis of influenza or pneumonia, including sputum and blood cultures, chest x-rays and blood tests. Influenza Health care providers usually will make the diagnosis of influenza based on symptoms and findings of a physical examination. Drugs that fight viruses (antivirals) are sometimes used in the management of flu. These drugs either shorten the duration of the flu, if taken early at the onset of the flu, or prevent the flu. There are currently four influenza antiviral drugs available in the United States: amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir and oseltamivir. Oseltamivir or zanamivir should be prescribed if an antiviral drug is indicated for the treatment of influenza. A recent study found that worldwide resistance to amantadine and rimantadine has increased 12 percent since the mid-1990s. Relenza has not been shown to shorten the length of influenza for this population and increases their risk of bronchospasm (wheezing) or serious breathing problems. These newer drugs can be used to treat strains from both the Type A and B influenza viruses. Over-the-counter medications can minimize discomfort associated with flu symptoms, but these medications do not treat the virus infection. Aspirin should not be used to treat flu symptoms in children under 18 years old because it may play a role in causing Reye Syndrome, a rare but severe liver and central nervous system condition. Congestion, cough and nasal discharge are best treated with a decongestant, an antihistamine or a combination of these two types of medication. Also, patients who have chronic medical conditions such as thyroid disease or high blood pressure should check with a health care provider before taking over-the-counter drugs for flu symptoms. Adequate liquids and nutrition are necessary for rapid recovery from the flu and to prevent dehydration. Frequent hand washing and mouth covering during coughing and sneezing helps to prevent transmission of the influenza virus.
The presence of purulent sputum during an exacerbation of symptoms is sufficient indication for starting empirical antibiotic treatment33 gastritis green stool gasex 100 caps. If an infectious exacerbation does not respond to the initial antibiotic treatment symptoms of gastritis flare up 100 caps gasex, a sputum culture and an antibiogram should be performed gastritis diet ���� generic gasex 100 caps online. Bio- chemical test abnormalities can be associated with an exacerbation and include electrolyte disturbance(s) gastritis journal pdf cheap gasex 100 caps overnight delivery. These abnormalities can also be due to associated co-morbid conditions (see below "Differential Diagnoses"). Even simple spirometric tests can be difficult for a sick patient to perform properly. These measurements are not accurate during an acute exacerbation; therefore their routine use is not recommended. These conditions include pneumonia, congestive heart failure, pneumothorax, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism, and cardiac arrhythmia. Noncompliance with the prescribed medication regimen can also cause increased symptoms that may be confused with a true exacerbation. There is not sufficient evidence, however, to indicate a difference in efficacy between the different classes of short-acting bronchodilators347, or to indicate additional benefit of combinations of short-acting bronchodilators348. However, if not already used, an anticholinergic can be added until the symptoms improve. One large study indicates that nebulized budesonide may be an alternative (although more expensive) to oral glucocorticosteroids in the treatment of non-acidotic exacerbations351. However, the exact criteria for this approach as opposed to hospital treatment remain uncertain and will vary by health care setting341-344. If it is determined that care can be initiated at home, this algorithm provides a stepwise therapeutic approach. Attempts at managing such patients entirely in the community have met with only limited success354, but returning them to their homes with increased social support and a supervised medical care package after initial emergency room assessment has been much more successful355. Venturi masks (high-flow devices) offer more accurate delivery of controlled oxygen than do nasal prongs but are less likely to be tolerated by the patient311. If a prompt response to these drugs does not occur, the addition of an anticholinergic is recommended, even though evidence concerning the effectiveness of this combination is controversial. Otherwise, the patient may be managed in the emergency department or hospital as detailed in Figure 5. Possible beneficial effects in terms of lung function and clinical endpoints are modest and inconsistent, whereas adverse effects are significantly increased363,364. There are no clinical studies that have evaluated the use of inhaled long-acting bronchodilators (either 2-agonists or anticholinergics) with or without inhaled glucocorticosteroids during an acute exacerbation. The exact dose that should be recommended is not known, but high doses are associated with a significant risk of side effects. Thirty to 40 mg of oral prednisolone daily for 7-10 days is effective and safe (Evidence C). Prolonged treatment does not result in greater efficacy and increases the risk of side effects. There was also some benefit in those patients with an increase in only two of these cardinal symptoms. The route of administration (oral or intravenous) depends on the ability of the patient to eat and the pharmacokinetics of the antibiotic. Doxapram, a nonspecific but relatively safe respiratory stimulant available in some countries as an intravenous formulation, should be used only when noninvasive intermittent ventilation is not available or not recommended377. Ventilatory support includes both noninvasive intermittent ventilation using either negative or positive pressure devices, and invasive (conventional) mechanical ventilation by oro-tracheal tube or tracheostomy. More importantly, mortality-or its surrogate, intubation rate-is reduced by this intervention380-383. Group C In patients at risk for pseudomonas infections: · Fluoroquinolonese (Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin high dosef) · Fluoroquinolonese (Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin high dosef) or · -lactam with P.
When computing the sum of squares gastritis diet xp gasex 100 caps without a prescription, you should always keep the calculations clearly labeled gastritis tratamiento cheap gasex 100 caps buy. The Ta symbol is used to avoid having to deal with too many L signs in our calculational procedures gastritis symptoms weakness buy 100 caps gasex otc. After Ta has been calculated gastritis nsaids discount 100 caps gasex mastercard, T~ is found by squaring Ta· Now, T~ is divided by na, the number of subjects in group a. Once the quantity T~/na has been computed for each group, the quantities are summed as indicated by the L symbol. Mean Squares After obtaining the sum of squares, it is necessary to compute the mean squares. Mean square stands for the mean ofthe sum ofthe squared deviations from the mean or, more simply, the mean of the sum of squares. The degrees of freedom are determined by the number of scores in the sum of squares that are free to vary. The greater the F value, the lower the probability that the results of the experiment were due to chance error. Statistical Tests 347 SignijU;ance ofP To determine the significance of the obtained Fvalue, it is necessary to compare the obtained Fto a critical value of F. To find the critical value of F, locate on the table the degrees of freedom for the numerator of the ratio (the systematic variance) and the degrees of freedom for the denominator of the Fratio (the error variance). The intersection ofthese two degrees offreedom on the table is the critical Fvalue. For the results to be significant, the obtained Fvalue must be equal to or greater than the critical value. ConcludingRemarks the analysis ofvariance for one independent variable with an independent groups design can be used when there are two or more groups in the experiment. Also, the calculations are the same whether the experimental or the correlational method is used to form the groups. The formulas are also applicable to cases in which the number of subjects in each group is not equal (although you should have approximately equal numbers of subjects in the groups). More complicated procedures for evaluating the difference between two groups in such designs are available, but these are beyond the scope of this book. Analysis of Variance: Two Independent Variables In this section, we will describe the computations for analysis of variance with a factorial design containing two independent variables. The formulas apply to an A X B factorial design with any number of levels of the independent variables. The formulas apply only to a completely independent groups design with different subjects in each group, and the number of subjects in each group must be equal. Once you understand this analysis, however, you should have little trouble understanding the analysis for more complicated designs with repeated measures of unequal numbers of subjects. Variable A is the type of instruction used in a course, and variable B is the intelligence level of the students. One class uses the traditional lecture method; the other class uses an individualized learning approach with frequent testing over small amounts of material, proctors to help individual students, and a stipulation that students master each section of material before going on to the next section. At the end ofthe course, all students take the same test, which covers all of the material presented in the course. This design allows us to evaluate three effects - the main effect of A, the main effect of B, and the A X B interaction. The main effect of A is whether one type of instruction is superior to the other; the main effect of B is whether highintelligence students score differently on the test than do low-intelligence students; the A X B interaction examines whether the effect of one independent variable is different depending on the particular level of the other variable. The procedures for calculation are similar to the calculations performed for the analysis of variance with one independent variable. The formula is where ~X2 is the sum of the squared scores of all subjects in the experiment, G is the grand total of all of the scores, and N is the total number of subjects. It is usually easiest to calculate ~X2 and G in smaller steps by calculating subtotals separately for each group in the design. Ths the sum ofthe squared totals ofthe scores in each ofthe groups of independent variable A, and na is the number of subjects in each level of independent variable A. In other words, the totals for each group of the A variable are obtained by considering all subjects in that level of A, irrespective of which condition of B the subject may be in. Each of the group totals is squared, and then the sum of the squared totals is obtained.
In the above example gastritis diet 6 small generic gasex 100 caps mastercard, we have outlined the kidneys in the second part of the figure gastritis diet ulcerative colitis generic 100 caps gasex visa, so that you can test your observation in this patient with unprepared bowel gastritis diet queen discount 100 caps gasex fast delivery. Even the experienced radiologist will often be unsure of their significance however gastritis meal plan gasex 100 caps buy, and it frequently takes additional imaging to exclude pathology. Note the similarity between the patient with a "normal" lobulated kidney vs the patient with renal pathology in the next illustrations. The lobulations may be the result of columns of Bertin or possibly the result of cortical parenchymal loss due to infarcts or previous bouts of pyelonephritis. A good history would be necessary to evaluate their current importance, but the lobulations are likely of no clinical significance. By the way- the right kidney in this patient is in an ectopic location in the pelvis and not visible in the coned-downed films to the left. Yellow arrow points to a bump on the left kidney of a patient that is more serious-this time a renal carcinoma as indicated by the neovascularity shown in the accompanying angiogram in Figure 85b (below). However, if it is seen to be in a lower position than the right kidney, that is a red flag to exclude displacement by either an enlarged spleen or some other retroperitoneal or intraperitoneal mass. Blue outlined arrow points to the lateral margin of the left kidney, which is seen to be in a lower position than the right kidney (red outlined arrows). This finding is a red flag to look for an enlarged spleen or other mass displacing the left kidney. The edge of the liver is also usually easily demarcated by the contrast of a water density organ bordered by peritoneal fat or gas filled bowel. The liver edge can also be silhouetted out by ascitic fluid and an enlarged liver can displace bowel inferiorly and to the left. If ascitic fluid is present the edge of the liver may disappear due to the silhouette sign. Note the spleenomegally and displaced left kidney in figure 86 on the previous page. The preperitoneal fat lines (the fourth item on the checklist) are thin lines of fat that outline the peritoneal reflections as demonstrated in figure 88. We have deliberately manipulated brightness and contrast in this image to demonstrate the band of fat density (red arrow) along the lateral margins of the abdomen. When fluid such as ascities or blood is present in the peritoneal cavity, the bowel gas is usually displaced away from the fat line. This phenomenon is called by radiologists "widening of the flank stripe" or " displacement of the fat line". Notice the increased distance between the preperitoneal fat (yellow arrows) and the edge of gas-filled bowel (red arrows) in this patient with ascities. Calcifications in the abdomen, the fifth item on the checklist, can be "Aunt Minnies" such as is seen in figure 90 in a patient with gallstones, or in figure 91 in a patient with a staghorn renal calculus. The red outlined arrow indicates a classic staghorn renal calculus in this "Aunt Minnie". Black arrows point to thin lines of calcium deposit in this patient with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Look for aortic and other vascular calcifications as a part of your routine in evaluating all abdominal films. Splenic artery aneurysms or pancreatic calcifications are another couple of "Aunt Minnies". More frequently, however, the student will be called on to search for a ureteral stone in a patient with renal colic or flank pain. See figure 93 for typical pancreatic calcifications (the location gives them away). Red outlined arrow points to large clusters of punctate calcifications in the location of the body of the pancreas consistent with chronic pancreatitis. The final item on the major checklist for the abdomen is the bony skeleton, and the same rule applies as it did for the chest, i. Just for practice see if you can spot the bony abnormality or abnormalities in figures 94-100 before reading the labeled answers. The white arrows indicate abscess formation in both psoas muscles in this child with spinal tuberculosis. Ignore the high contrast (white bone) in this reproduction and concentrate on cortical outlines.
Gasex 100 caps without a prescription. How Acid Reflux Works Animation Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms Causes Video Endoscopy GERD.
References
- Snoeck R, Bossens M, Parent D, et al: Phase II double-blind placebo-controlled study of the safety and efficacy of cidofovir topical gel for the treatment of patients with human papillomavirus infection, Clin Infect Dis 33:597n602, 2001.
- Lee JY, Kim HW, Lee SJ, et al: Comparison of doxazosin with or without tolterodine in men with symptomatic bladder outlet obstruction and an overactive bladder, BJU Int 94(6):817, 2004.
- Lynch JA, Parimi N, Chaganti RK, Nevitt MC, Lane NE. The association of proximal femoral shape and incident radiographic hip OA in elderly women. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2009; 17(10):1313-18.
- Catella-Lawson F, Reilly MP, Kapoor SC, et al. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors and the antiplatelet effects of aspirin. N Engl J Med 2001;345(25):1809-17.
- Miller GA, Sutton GC, Kerr IH, Gibson RV, Honey M. Comparison of streptokinase and heparin in treatment of isolated acute massive pulmonary embolism. Br Med J. 1971;2:681-684.
- FDA releases final guidance for pharmacogenomic data, Pharmacogenomics 6:209, 2005.
- Liu K, Wen G, Lv XF, et al. MR imaging of cerebral extraventricular neurocytoma: a report of 9 cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2013; 34(3):541- 546.