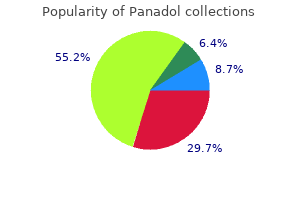
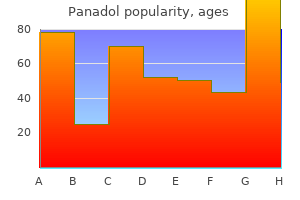
Panadol
Matthew Stephen Boulos, DO
- Medical Instructor in the Department of Medicine

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/matthew-stephen-boulos-do
Prevalence of subjective poor health symptoms associated with exposure to electromagnetic fields among university students medications varicose veins . Re: "effects upon health of occupational exposure to microwave radiation (radar)" symptoms rheumatic fever . Cerenkov ultraviolet radiation (137Cs gamma-rays) and direct excitation (137Cs gamma-rays and 50 kVp X-rays) produce photoreactivable damage in Escherichia coli medicine review . Effects of acute exposure to the radiofrequency fields of cellular phones on plasma lipid peroxide and antioxidase activities in human erythrocytes medicine 79 . Evaluation of occupational risk for health of operators of petrochemical production and their physiological and hygienic stipulation. Occurrence and risk of cochleotoxicity in cystic fibrosis patients receiving repeated high-dose aminoglycoside therapy. Re: "Exposure to residential electric and magnetic fields and risk of childhood leukemia" and "case-control study of childhood cancer and exposure to 60-Hz magnetic fields". Radiation therapy planning of a breast cancer patient with in situ pacemaker-challenges and lessons. Pulsed Electromagnetic Field Stimulation Promotes Anti-cell Proliferative Activity in Doxorubicin-treated Mouse Osteosarcoma Cells. Super-low frequency electric and magnetic fields and their role in development of neoplasms. Primary brain cancer in adults and the use of common household appliances: a case-control study. Relevance of in vitro studies for the immunity of cardiac implants in an electromagnetic field environment. Bioeffects of electromagnetic fields-safety limits of each frequency band, especially less than radio one. Overtreatment effects associated with a radiofrequency tissue-tightening device: rare, preventable, and correctable with subcision and autologous fat transfer. Occupational exposure to physical agents: the new Italian database for risk assessment and control. Measurement of thermal effects on the optical properties of prostate tissue at wavelengths of 1,064 and 633 nm. Ultrasound-guided radiofrequency-assisted segmental arterioportal vascular occlusion in laparoscopic segmental liver resection. Laparoscopic blood-saving liver resection using a new radiofrequency-assisted device: preliminary report of an in vivo study with pig liver. Need for a European approach to the effects of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on cancer. Interactions of radiofrequency radiation on 2-methoxyethanol teratogenicity in rats. Interactive developmental toxicity of radiofrequency radiation and 2methoxyethanol in rats. Developmental toxicity interactions of salicylic acid and radiofrequency radiation or 2-methoxyethanol in rats. Influence of high-voltage ignition systems on the function of implanted pacemaker. Feasibility of future epidemiological studies on possible health effects of mobile phone base stations. When "wire codes" predict cancer better than spot measurements of magnetic fields. Effects of information and 50 Hz magnetic fields on cognitive performance and reported symptoms. Exposure to static electric fields leads to changes in biogenic amine levels in the brains of Drosophila. Study of narrow band millimeter-wave potential interactions with endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor genes.
Authors suggested that hypothermia was not induced quickly enough to produce a benefit in normothermic patients symptoms jock itch , and that rewarming patients who arrived hypothermic was detrimental medicine technology . Follow-up was completed for enrolled patients medicine news , and exploratory subgroup analyses revealed that in patients with surgically removed hematomas the hypothermia group had better outcomes medicine under tongue , while in patients with diffuse brain injuries there was no significant difference in outcomes. These findings suggest a potential underlying reason for the null finding, but would need to be tested in studies designed to determine if there is a difference in outcome for different types of patients before it could be used to inform evidence-based recommendations. For example, patients in the later study reached target temperatures earlier than those in the first study, in which the time to target temperature was mixed. For this analysis, the authors compared patients who were cooled more quickly, within 1. While other studies also compared hypothermia to normothermia, they differed in important ways. The hypothermia group was kept cool for 3 to 5 days and had lower mortality rates. One study randomized 215 patients at three medical centers to long-term and short-term hypothermia. Lui, 2006 conducted a preliminary study that compared head only (selective brain cooling) with full body (systemic cooling) and normothermia. Class 3 Studies the summary of evidence from Class 3 studies of prophylactic hypothermia is summarized in Table 2-3. Complications (pulmonary infection, urinary tract infection, and thrombocytopenia) were not significantly different. Four reported better neurological 46 outcomes in patients treated with hypothermia,20-22,24 while two found no difference. High rates of prasugrel and ticagrelor nonresponder in patients treated with therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest. Brain Trauma Foundation, American Association of Neurological Surgeons, Congress of Neurological Surgeons, et al. Comparison of hypothermia and normothermia after severe traumatic brain injury in children (Cool Kids): a phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Effect of long-term mild hypothermia or short-term mild hypothermia on outcome of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Effects of selective brain cooling in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: a preliminary study. Moderate hypothermia improves imbalances of thromboxane A2 and prostaglandin I2 production after traumatic brain injury in humans. Effect of long-term mild hypothermia therapy in patients with severe traumatic brain injury: 1-year follow-up review of 87 cases. Early induction of hypothermia for evacuated intracranial hematomas: a post hoc analysis of two clinical trials. Discrete cerebral hypothermia in the management of traumatic brain injury: a randomized controlled trial. Applying cerebral hypothermia and brain oxygen monitoring in treating severe traumatic brain injury. Effects of therapeutic mild hypothermia on patients with severe traumatic brain injury after craniotomy. Noninvasive selective brain cooling by head and neck cooling is protective in severe traumatic brain injury. Mild hypothermia therapy reduces blood glucose and lactate and improves neurologic outcomes in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. The landmark work of Weed and McKibben4 disproved this long-held dogma when they demonstrated dramatic changes in the volume of the brain resulting from administration of hypertonic or hypotonic intravenous solutions. Since that time, intravenous administration of hyperosmolar agents has become routine in the management of intracranial hypertension and herniation syndromes. Mannitol and hypertonic saline are routinely employed hyperosmolar agents in North America.
Studies variously interpret cases as a neurophysiological response symptoms you have cancer , a hyper-suggestible state medications 230 , or a mechanism for expressing low self-image symptoms xanax . On-lookers usually find such imitative episodes amusing symptoms 6 days after embryo transfer , while victims feel humiliated. Research links the condition to stress, anger, emotional distress, and low selfesteem. Cases are traditionally treated with herbal teas, "nerve pills", rest, isolation, and family support. Culturally interpreted symptoms or culture-bound syndromes: a cross-cultural review of nerves. Fears are reinforced by cultural views of the condition as a legitimate humoral disorder. Overview of mental disorders in Chinese cultures: review of epidemiological and clinical studies. Pibloktoq, Arctic hysteria (Inuits living within the Arctic Circle) Prodromal fatigue, depression, or confusion, followed by a "seizure" of disruptive behaviour, including stripping or tearing off clothes, frenzied running, rolling in snow, glossolalia or echolalia, echopraxia, property destruction, and coprophagia. Most episodes last only minutes and are followed by loss of consciousness, amnesia, and complete remission. Injury is rare and, while some studies have related cause to hypocalcaemic tetany, most researchers link incidents to interpersonal anxieties and cultural stressors. Susto, espanto (Mexico, Central and South America) Highly diverse, chronic complaints attributed to "soul loss" induced by a severe, often supernatural, fright. Symptoms often include agitation, anorexia, insomnia, fever, diarrhoea, mental confusion and apathy, depression, and introversion. Studies variously attribute cases to hypoglycaemia, nonspecific organic disease, generalized anxiety, and stress resulting from social conflict and low self-esteem. Toward a meaning-centered analysis of popular illness categories: fright illness and heart distress in Iran. The study of disease in relation to culture - the susto complex among the Mixe of Oaxaca. Taijin kyofusho, shinkeishitsu, anthropophobia (Japan) Anxiety or phobia more common among men and young adults. Cases are marked by a fear of social contact (especially friends), extreme self-consciousness (concern about physical appearance, body odour, blushing), and a fear of contracting disease. Victims, popularly regarded as highly intelligent and creative, may display perfectionist tendencies. Studies suggest cultural values encourage "over-socialization" of some children, producing feelings of inferiority and anxiety in social situations. Features include shouting, sobbing, repeated neologisms, paralysis, convulsions, and a trance-like stupor or loss of consciousness. Some experience nightmares with sexual themes or rare episodes of temporary blindness. Attacks, which can continue for days or weeks, may be provoked by the sight of men or foreigners. Uqamairineq (Inuits living within the Arctic Circle) Sudden paralysis associated with borderline sleep states, accompanied by anxiety, agitation, or hallucinations. While the condition is usually chronic and can prompt panic, most attacks last only minutes and are followed by complete remission. Cases are fairly common, and traditionally alleged to result from soul loss, soul wandering, or spirit possession. Studies describe the experience as a dissociative hysterical reaction and possible variant of the narcolepsy-cataplexy syndrome. Windigo (various spellings) (indigenous people of north-east America) Rare, historic accounts of cannibalistic obsession. Traditionally, cases were ascribed to possession, with victims (usually male) turning into cannibal monsters. Symptoms included depression, homicidal or suicidal thoughts, and a delusional, compulsive wish to eat human flesh. Early research described episodes as hysterical psychosis, precipitated by chronic food shortages and cultural myths about starvation and windigo monsters.
. Gallstones- symptom causes type risk factors and complications.
Diseases
- Hereditary nodular heterotopia
- Braddock Jones Superneau syndrome
- Congenital toxoplasmosis
- Muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral
- Myocardium disorder
- Pseudo-Gaucher disease
- Progressive kinking of the hair, acquired
- Cranioectodermal dysplasia
References
- Stephens D: Caecoureterocele and concepts on the embryology and aetiology of ureteroceles, Aust N Z J Surg 40(3):239n248, 1971.
- Alberio L, Dale GL. Review article: platelet-collagen interactions: membrane receptors and intracellular signalling pathways. Eur J Clin Invest. 1999;29(12):1066-1076.
- Simpson JL, Powell H, Boyle MJ, et al. Clarithromycin targets neutrophilic airway inflammation in refractory asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2008; 177: 148-155.
- Ellershaw J, Ward C. Care of the dying patient: the last hours or days of life. BMJ 2003;326(7379):30-34.