Alphagan
Joseph F. Golob MD
- Resident in Surgery, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine,
- Department of Surgery, MetroHealth Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio
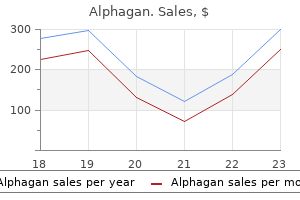
Treatment with lurasidone was associated with significantly increased serum levels of glutamate medicine vending machine , glycine and serine compared to placebo as well as olanzapine treatment medications without a script . In contrast to lurasidone treatment xdr tb , olanzapine significantly inhibited the activity of oxidoreductases/dehydrogenases and significantly increased sugar alcohol/polyols medications overactive bladder . Olanzapine also significantly decreased serum essential, long chain fatty acids, and carnitines. Conclusion: Data obtained from serum metabolomic profiling from a lurasidone clinical trial are consistent with the hypothesis based on its pharmacological profile that lurasidone treatment may be associated with enhanced glutamate activity. These data also suggest significant differences in the metabolome exist in subjects treated with lurasidone and olanzapine. Metabolomics: A global biochemical approach to the study of central nervous system diseases. Superiority of asenapine over olanzapine was observed in 1 of the extensions but not in the other extension or in either of the core studies. Methods: the 2 core studies and their respective extensions were doubleblind, doubledummy, olanzapinecontrolled trials. Of the 613 participants (asenapine, n=277; olanzapine, n=336) who completed 26 weeks of treatment, 502 (asenapine, n=220; olanzapine, n=282) entered a 26week extension and 412 (asenapine, n=170; olanzapine, n=242) completed an additional 26 weeks of treatment. Results: Discontinuation due to lack of therapeutic effect was significantly greater with asenapine vs olanzapine for the first 26 weeks for core study participants (13. However, these results need to be interpreted in view of the fact that a large portion of participants did not enter the extension studies and those who did enter the extension continued treatment without rerandomization. This study focuses in the phenomenon of delusional selfmisidentification, which has been scarcely documented. Neurobiological models, as informed by clinical disturbances including asomatognosia, somatoparaphrenia and mirrored selfmisidentification, have supported a unitary and localizationist view of the self. The description of patients without structural damage, who persistently deny their identity but construct a delusional one, provides a rational basis for a shift towards multidimensional models of selfhood and personal identity. One of the central purposes of crosscultural psychiatry is to scrutinize the sociocultural influences on the phenomenology of mental disorders. We also have chosen to evaluate the ompact of personal relogiosity on the psychotic phenomena, as Lithuania is known as a Catholic country. After long years of the Soviet occupation, along with political and economical changes, Lithuania has become a region undergoing cultural shock, what is interesting and valuable for psychiatric research. In this situation, cultural assessment should be essential in order to a better understanding of psychiatric patients. We present here the data of phenomenology of Religious and Apocalyptic delusions, and visual hallucinatios. Personal importance of faith was not confirmed as an independent predictor of religious delusions in patients with schizophrenia, but marital status and educational level. Female patients most often considered themselves as Saints, whereas male patients most often considered themselves as being a God. Schizophrenia patients for whom their faith is of personal importance feel the coming end of world more often than those for whom it is not. Higher prevalence of the world end delusions was found among divorced patients as compared to those who lived in the family. Female patients reported the world end delusions with religious content (apocalyptic) more often than the male patients. Male patients as compared to female patients more often reported world end delusion with global content. Patients with schizophrenia for whom their faith was of personal importance compared to patients with schizophrenia for whom their faith was not of personal importance had higher prevalence of visual hallucinations. The early onset of illness (age until 20) and personal importance of faith were independent predictors of development of visual hallucinations. However, the cognitive profile of the samples is relevant in both, the degree of deterioration and the areas of deficits, as they relate differentially to both functional outcome and quality of life. Purpose: To analyse the profile of cognitive decline in a broad sample of patients to identify specific profiles associated to the clinical diagnosis and phase of the illness. Data suggest that these and no other, specific domains are more sensitive to the decline with the years of evolution of the illness, increased number of hospitalizations, and treatment adherence. This decline is significantly higher than the general decline shown in normal population.
Motor disturbances include "wing-beating" tremor or asterixis medications you can crush , dysarthria medications like gabapentin , unsteady gait medicine shoppe , and rigidity medications gabapentin . Another disease commonly referred to as a disease of the basal ganglia is tardive dyskinesia. This disease indeed involves the basal ganglia, but it is caused by medical treatment of another disorder with neuroleptic drugs such as phenothiazides or haloperidol. Long-term use of these drugs may produce biochemical abnormalities in the striatum. The motor disturbances include either temporary or permanent uncontrolled involuntary movements of the face and tongue and cogwheel rigidity. Prolonged drug use leads to hypersensitivity of D3 dopaminergic receptors and an imbalance in nigrostriatal influences on motor control. Possibly because of the interconnections of this nucleus with the frontal portions of the neocortex, lesions of the caudate nuclei disrupt performance on tests involving object reversal and delayed alternation. In addition, lesions of the head of the left but not the right caudate nucleus and nearby white matter in humans are associated with a dysarthric form of aphasia that resembles Wernicke aphasia. When one or more of these pathways become dysfunctional, characteristic motor abnormalities occur. Diseases of the basal ganglia lead to two general types of disorders: hyperkinetic and hypokinetic. The hyperkinetic conditions are those in which movement is excessive and abnormal, including chorea, athetosis, and ballism. Choreiform and athetotic movements have been likened to the start of voluntary movements occurring in an involuntary, disorganized way. In addition to Parkinson disease, which is described below, there are several other disorders known to involve a malfunction within the basal ganglia. Huntington disease is one of an increasing number of human genetic diseases affecting the nervous system that are characterized by trinucleotide repeat expansion. There is also preliminary evidence that increased numbers of a 12-nucleotide repeat are associated with a rare form of epilepsy. Parkinson disease is the first disease identified as being due to a deficiency in a specific neurotransmitter. In the 1960s, Parkinson disease was shown to result from the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Parkinsonism now occurs in sporadic idiopathic form in many middle-aged and elderly individuals and is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases. Dopaminergic neurons and dopamine receptors are steadily lost with age in the basal ganglia in normal individuals, and an acceleration of these losses apparently precipitates parkinsonism. Parkinsonism is also seen as a complication of treatment with the phenothiazine group of tranquilizer drugs and other drugs that block D2 receptors. The hypokinetic features of Parkinson disease are akinesia and bradykinesia, and the hyperkinetic features are cogwheel rigidity and tremor at rest. The absence of motor activity and the difficulty in initiating voluntary movements are striking. There is a decrease in the normal, unconscious movements such as swinging of the arms during walking, the panorama of facial expressions related to the emotional content of thought and speech, and the multiple "fidgety" actions and gestures that occur in all of us. The rigidity is different from spasticity because motor neuron discharge increases to both the agonist and antagonist muscles. Passive motion of an extremity meets with a plastic, dead-feeling resistance that has been likened to bending a lead pipe and is therefore called lead pipe rigidity. Sometimes a series of "catches" takes place during passive motion (cogwheel rigidity), but the sudden loss of resistance seen in a spastic extremity is absent. The tremor, which is present at rest and disappears with activity, is due to regular, alternating 8-Hz contractions of antagonistic muscles. This balance between inhibition and excitation somehow maintains normal motor function. The overall increase in inhibitory output to the thalamus and brain stem disorganizes movement. The parts are distorted to show the cerebellar peduncles and the way the cerebellum, pons, and middle peduncle form a "napkin ring" around the brain stem. Some improvement is produced by decreasing the cholinergic influence with anticholinergic drugs.
. Pregnancy Symptoms ??| New #Symptom | #Flu Symptoms | Tired Uterus?.
As former cues are reintroduced when they begin to take visits into the community past pubs and off-licenses medicine omeprazole , and re-establish former friendships and generally become more active medicine questions , drinking behaviour often returns abro oil treatment . Nevertheless medications to avoid during pregnancy , there may be a tendency for the proportion of patients with drinking problems to decrease after brain injury (Kreutzer et al. In the year before 41% were rated as heavy drinkers, but this had reduced to 17% in the year following injury. They found little evidence of new cases of alcohol dependence arising in the post-injury year. However, when followed up for 30 years almost 12% of patients were found to have developed alcohol abuse not previously present (Koponen et al. In a study looking particularly at drug abuse, there is evidence that there may be some who only take to drug abuse after the injury, and might not have done so had they not been injured (Hibbard et al. Location of brain damage incurred Many investigations have sought to determine how far psychiatric disability depends on the location of damage within the brain. Studies examining the correlations between neuroimaging and outcome in closed head injury are discussed in Neuroimaging and head injury, earlier in chapter. On the other hand, penetrating injuries are more suitable for analysis, though even here it must be recognised that damage may exist where it is unsuspected. Teuber (1959, 1962) and coworkers investigated cognitive and perceptual defects in a large series of penetrating injuries with regional brain damage. Among unilateral wounds, the left were associated with more psychiatric disturbance than the right, particularly where dementias and psychoses were concerned. Patients with parietal, occipital and cerebellar lesions were relatively free from psychiatric disturbance. Lishman (1968) also found left hemisphere lesions to be more closely associated with overall psychiatric disability than right hemisphere lesions and patients with injury to the left temporal lobe were particularly at risk. However, intellectual disorders were found more commonly after left hemisphere damage, while affective disorders, behavioural disorders and somatic complaints were more frequent after right hemisphere damage (Table 4. Intellectual disorders were especially associated with damage to the parietal and temporal lobes, whereas affective disorders, behavioural disorders and somatic complaints were more frequent after frontal lobe damage. Sexual disturbances were seen only after frontal wounds, and with one exception this was also Head Injury Table 4. In the Vietnam Head Injury Study, right orbitofrontal injury was associated with increased edginess, anxiety and depression, whereas left dorsolateral frontal lesions showed greater anger and hostility (Grafman et al. The literature on the behavioural consequences of patients suffering head injuries in the world wars, which also demonstrated locaton-specific effects, will be reviewed in detail below. There is therefore support for the broad generalisation that lesions in some areas provide a greater psychiatric hazard than others, and that this involves emotional and behavioural disturbances as well as cognitive defects. Nevertheless, it seems likely that in general the amount of brain damage incurred is more important than its location in determining outcome (Grafman et al. Categories of post-traumatic psychiatric disorder the many different forms of post-traumatic psychiatric disablement cannot be rigidly classified, and complex admixtures of symptoms are frequently seen. For example, changes of temperament may occur along with intellectual impairment, or paranoid developments may arise in association with neurotic disability. Quite often, however, specific features or a combination of related features are outstanding, or even seen in relative isolation. For this reason the four main categories of psychiatric disturbance are examined separately: cognitive impairment, change of personality, psychosis, and affective disorders. The problem of the so-called post-concussion syndrome will be dealt with separately, alongside a discussion of outcome after mild head injury. The relative frequency of these changes may be gauged from the analysis of two large series of patients in which these broad divisions have been observed. The frequency of cognitive impairment will depend heavily on the severity of brain injury studied. For example, half of patients with severe head injury will have memory impairment (Levin 1990). More recently, standardised diagnostic assessments have ascertained the frequency of Axis 1 mental disorders after closed head injury. High rates of depression and anxiety disorders were identified in patients with a head injury attending a brain injury rehabilitation outpatient clinic; 26% had a major depressive disorder and 24% generalised anxiety disorder (Fann et al. Comorbidity is common; in one study half of patients with major depression also had generalised anxiety disorder (van Reekum et al.
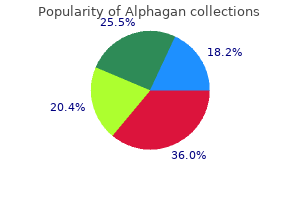
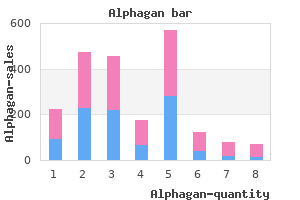
All diagnoses for each category were counted to calculate the percentage of diagnostic categories that met hypovitaminosis D cutoff values k-9 medications . Vitamin D levels in 21% of patients were below 20 ng/mL medications names , compared to 14% in general population treatment 4 sore throat . While no statistical conclusions regarding diagnoses can be made treatment goals and objectives , there was a trend towards greater deficiency among psychotic disorders which is consistent with available literature reviews. Larger studies utilizing stringent diagnostic measures are required to characterize the extent of hypovitaminosis D among psychiatric patients, potential pathologic and treatment relationships, and guidelines for screening. Methods the 20 study participants were patients in an acute inpatient psychiatric unit. Both groups will receive an article from a classic psychiatric journal selected by the Principal Investigator, with the request that residents will read and be prepared to discuss the content in an hour long discussion. One of the randomized groups will receive the traditional paper form of the article placed in their mailbox, while the other will receive a password protected. A questionnaire will be distributed to assess compliance with reading the article and core competencies. After two trials, a crossover design will be employed for control purposes with subsequent distribution of novel journal articles for discussion. This project is intended as a pilot study to determine if there are differences in resident compliance with reading a journal article based upon method of distribution as well as individual preference. With the results of this study, the effect size of information distribution method on resident compliance to assigned education activities may be determined with a plan for a larger subsequent power study involving other psychiatry residency programs to test for significance with each distribution method. The Use of the World Wide Web by Medical Journals in 2003 and 2005: An Observational Study. One possible explanation for its limited utilization may be the lack of exposure during residency and fellowship training. Method: A 17item electronic survey was distributed to directors or administrators of 485 psychiatry residency and fellowship training programs in the United States who were then asked to voluntarily distribute the survey to their residents and fellows. Of these, 72% reported being very interested or interested in telepsychiatry, while only 29% reported that they planned to utilize telepsychiatry in their practice after training. The majority of respondents (78%) agreed that exposure to telepsychiatry was an important aspect of training and over half of the respondents (51%) felt that it should be required. Of the 52 respondents (18%) who had clinical exposure to telepsychiatry, 36 (72%) reported that their experience increased their interest level and 33 (66%) reported having either a onetime encounter or five hours or less of direct patient care via telepsychiatry. Clinical exposure to telepsychiatry was significantly related to level of training (p=0. The availability of didactic experiences, clinical exposure time, and exposure setting did not significantly influence future plans to use telepsychiatry. Conclusions: these results reveal a practice gap between resident interest and exposure to telepsychiatry. Training programs may want to consider incorporating a brief telepsychiatry experience early in training to fulfill both resident interest and the growing demand for psychiatric physicians. It is estimated that medical students obtain onethird of their knowledge from residents. It is also welldocumented that an effective resident teacher can influence the future career choice of a medical student. Potential barriers to medical student education are divided into those that are systemsbased and individualbased. Objectives: this project aims to eliminate many of the barriers to resident teaching of medical students by providing role modeling, clear objectives, and recognition. It is hypothesized that the motivation of residents to teach will be increased through this intervention of friendly competition. Study Design: Each psychiatry clerkship block is set up as a fantasy football game. Teams of three to four residents led by a faculty member compete against each other to accumulate the most points over the sixweek rotation.
References
- Ferns SP, Sprengers ME, van Rooij WJ, et al. Coiling of intracranial aneurysms: a systematic review on initial occlusion and reopening and retreatment rates. Stroke 2009;40(8):e523-9.
- Yilmaz AT, Arslan M, Demirklic U, et al: Late posterior cardiac tamponade after open heart surgery, J Cardiovasc Surg 37:615, 1996.
- Maruyama M. Management of electrical storm: the mechanism matters. J Arrhythmia. 2014;30:242-249.
- Sawaki Y, Ohkubo H, Hibi H, Ueda M. Mandibular lengthening by distraction osteogenesis using osseointegrated implants and an intraoral device: a preliminary report. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54:594-600.
- Waern AU, Anderson P, Hemmingsson A: Takayasu's arteritis: a hospital-region based study on occurrence, treatment, and prognosis, Angiology 34:311, 1983.
- McKay RR, Kroeger N, Xie W, et al: Impact of bone and liver metastases on patients with renal cell carcinoma treated with targeted therapy, Eur Urol 65(3):577n584, 2014.