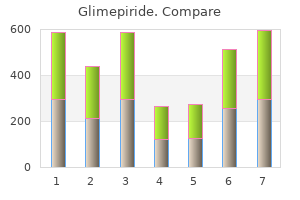
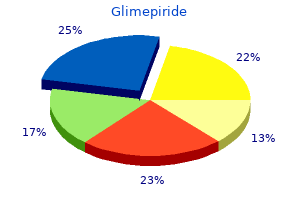
Glimepiride
Khaled N. Almusrea, MBBS, FRCSC
- Chairman, Spine Surgery Department
- Subspecialty Consultant Neurosurgeon, Spine Surgeon
- Department of Spine, Department of Neurosurgery
- Neurosciences Center
- King Fahd Medical City
- Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Vaccine virus was shed by 9% of 360 infants after dose 1 diabetes education services purchase 4 mg glimepiride visa, but none of 249 and 385 infants after doses 2 and 3 diabetes symptoms at 30 buy generic glimepiride 4 mg online, respectively diabetes testing supplies buy cheap glimepiride 2 mg line. Each 1-mL dose of reconstituted vaccine contains at least 106 median cell culture infective units of virus diabetes test products glimepiride 1 mg purchase amex. Fecal shedding of rotavirus antigen was evaluated in all or a subset of infants from seven studies in various countries. After dose 2, rotavirus antigen shedding was detected in 4% to 18% of infants at approximately day 7, and 0 to 1. Duration of Immunity the duration of immunity from rotavirus vaccine is not known. The vaccination series for both vaccines may be started as early as 6 weeks of age. Subsequent doses in the series should be separated from the previous dose by 1 to 2 months. Rotavirus vaccine should be given at the same visit as other vaccines given at these ages. This difference, as well as the different number of doses in the series could complicate decisions by clinicians who encounter children who received a brand of rotavirus vaccine other than the brand the clinician has in stock. No rotavirus vaccine should be administered to infants older than 8 months 0 days of age. But if the interval is prolonged, the infant can still receive the vaccine as long as it can be given on or before the 8-month birthday. It is not necessary to restart the series or add doses because of a prolonged interval between doses. There are few data on the safety or efficacy of giving more than one dose, even partial doses, close together. However, vaccination should not be deferred if the product used for a prior dose or doses is not available or is not known. In this situation, the provider should continue or complete the series with the product that is available. There are at least 5 serotypes of rotavirus that may cause diarrheal disease in the United States. In addition, infants may experience multiple episodes of rotavirus diarrhea because the initial infection may provide only partial immunity. Infants documented to have had rotavirus gastroenteritis before receiving the full course of rotavirus vaccinations should still begin or complete the 2- or 3-dose schedule. Contraindications and Precautions to Vaccination 18 Rotavirus vaccine is contraindicated for infants who are known to have had a severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic) to a vaccine component or following a prior dose of vaccine. Some, but not all, postmarketing studies of the currently licensed vaccines have detected an increased risk for intussusception following rotavirus vaccine administration, particularly during the first week following the first dose of vaccine. Children who are immunocompromised because of congenital immunodeficiency, or hematopoietic stem cell or solid organ transplantation sometimes experience severe, prolonged, and even fatal rotavirus gastroenteritis. However, no safety or efficacy data are available regarding administration of rotavirus vaccine to infants who are, or are potentially immunocompromised due to either disease or drugs. Second, vaccine strains of rotavirus are considerably attenuated, and exposure to an attenuated rotavirus is preferable to exposure to wild-type rotavirus. Rotavirus vaccine should generally not be administered to infants with acute, moderate or severe gastroenteritis, or other acute illness until the condition improves. However, infants with mild acute gastroenteritis or other mild acute illness can be vaccinated, particularly if the delay in vaccination will delay the first dose of vaccine beyond 15 weeks 0 days of age. No data are available on the immune response to rotavirus vaccine in infants who have recently received a blood product. In theory, infants who have recently received an antibody-containing blood product might have a reduced immunologic response to a dose of oral rotavirus vaccine. In clinical trials, rotavirus vaccine appeared to be generally well tolerated in preterm infants, although a relatively small number of preterm infants have been evaluated. So if an infant were to be vaccinated with rotavirus vaccine while still needing care in the hospital, a theoretic 18 271 Rotavirus risk exists for vaccine virus being transmitted to infants in the same unit who are acutely ill, and to preterm infants who are not age eligible for vaccine. Although rotavirus is shed in the feces of vaccinated infants transmission of vaccine virus has not been documented. Infants living in households with persons who have or are suspected of having an immunodeficiency disorder or impaired immune status can be vaccinated. Infants living in households with pregnant women should be vaccinated according to the same schedule as infants in households without pregnant women.
Hospitalization appearance due to Nominal pneumonia through their lives without counting the actual diabetes medications dpp 4 glimepiride 1 mg online, and the age in which the event happened managing diabetes and copd discount glimepiride 1 mg line. Does not know X months Personal Pathological backgrounds Health problem Control Specified health Control problem Hospitalizations Control background due to diarrhea Age at the Control moment of the previous hospitalization due to diarrhea Hospitalization Control background due to pneumonia diabete alta sintomas generic glimepiride 4 mg otc. Quantity of days with diarrhea diabetes insipidus urine sodium level 2 mg glimepiride purchase with visa, from the beginning of the episode to the medical attention. Maximum amount of evacuations decreased in consistency by day Characteristics quality required in terms of firmness and stool complement. Quantitative Discrete Quantitative Discrete Quantitative discrete Quantitative discrete Nominal polytomous Number of days 1 to X 1 to X 1 Pasty 2 Semi liquid 3 Liquid 1 No 2 Only mucus 3 Only Blood 4 Mucus and blood 1. Maximum amount of vomit events a day Maximum body temperature registered from the minor during the diarrheic episode. Corporal weight of the minor in kilograms determined at the moment of the interview. Clinical manifestation that the subject presents in relation with their alert state. Continuous Open alphanumeric chain Physical exploration at the moment of the initial assessment Weight Control Kilograms Height Control Continuous Centimeters General condition Control Qualitative nominal Eyes Control Presence or absence of sunken eyes Nominal secondary to the dehydration polytomous caused by diarrhea. Oral mucosa Control Level of dehydration of the oral and Nominal tongue mucosa, excluding lips. Urgent care Treatment Area of contact first Control Area of the hospital where the minor Nominal received the first medical attention polytomous for this episode od diarrhea. Ambulatory with oral treatment consisting on the polynomial hydration reposition of the liquids lost during 2. Urgent care with oral the episodes of diarrhea via enteral hydration before going to medical attention. Hospitalized Presence or absence of the antibiotic Nominal 1 Yes prescription in their current dichotomous 2 No condition. Type of antibiotic that was Nominal Alphanumeric prescribed for their current condition. Presence or absence of the prescription of other medications for their actual condition. Quantitative discrete Nominal dichotomous Nominal 1 to X 1 Yes 2 No Alphanumeric of Control Control of Control Control Nominal Quantitative discrete Nominal dichotomous Nominal Alphanumeric 1 to X 1 Yes 2 No Alphanumeric Control Antidiarrheal Control dosage Days with Control antidiarrheal Other treatment Control Nominal Quantitative discrete Nominal dichotomous Nominal Alphanumeric 1 to X 1 Yes 2 No Alphanumeric Name lactobacilli of Control Protocol Version 2. Does not know Day-monthyear Date sample of Control stool Specification of a day in the Quantitative calendar, in which the fecal matter continuous was taken. Hour of the day in which the Quantitative recollection of stool samples continuous initiated. Name of the person that provided Nominal Alphanumeric the information of the minor. Nominal dichotomous Nominal dichotomous Control Control Control Clinical manifestation that the Qualitative subject presents in relation with nominal their alert state. Does not know No Yes, only liquids Yes, liquids and solids Ingested with no problem Had difficulty, specify Yes No Alphanumeric Protocol Version 2. Maximum amount of evacuations Quantitative 1 to X decreased in consistency per day. No Quantity of days with vomit, from Quantitative 1 to X the start of the episode up to the discrete medical attention. Quantitative continuous Discrete Alphanumeric open 0 to X g/dL Concentrations of zinc in blood/serum at the beginning of study. Time tracking the Control or Time in days since the beginning of sample independent symptoms/start of the treatment/clinical cure/end of the supplementation? Levels of zinc Dependent Blood concentration/ zinc serum in tracking g/dl in a time X determined. Basal albumin Control Serum concentrations of albumin in blood at the beginning of the study. Hemoglobin Control Hemoglobin concentration in blood at the beginning of the study. Levels of basal Independent Zinc Hours Quantitative Continuous Quantitative continuous Quantitative continua 0 to X g/dL 0 to X gr/dL 0 to X g/dL Analysis Plan the analysis of the results will be by protocol and by intention to treat.
Glimepiride 1 mg buy. Richtige Ernährung kann Diabetes Typ 2 heilen | Die Ernährungs-Docs | NDR.
Among potential toxicities diabetes diet for weight loss 4 mg glimepiride buy with visa, hepatic toxicities are one for which routine surveillance should be initiated metabolic disease center generic glimepiride 4 mg buy on-line. If the levels of liver transaminases increase to 3 to 5 times above normal diabetes test h1 quality glimepiride 1 mg, the androgen dose should be tapered until the blood tests improve diabetes uk cheap glimepiride 4 mg free shipping. Even without additional risk factors, malignant transformations may occur after years of androgen treatment (32). Importantly, low absolute neutrophil counts that occur in isolation and are not associated with bacterial infections are not an indication for cytokine treatment. It is reasonable to monitor the bone marrow morphology and cytogenetics every 6 months while patients are treated with cytokines. It might be especially important for patients who fail to respond to androgens or cytokines, who have no acceptable transplant donor, or who have an unacceptably high transplant risk (see Chapter 11). This will give families the opportunity to initiate transplant at a time that is optimal for the patient and also the family. It remains unclear whether chemotherapy prior to transplant improves or worsens outcomes. Hemoglobin levels should be monitored closely, as outlined above, so that treatment may be instituted before transfusion with packed red blood cells is required. Patients with cardiorespiratory problems in addition to anemia also have elevated baseline hemoglobin levels and may require a higher threshold Hgb value for recognition of failing erythropoiesis and for treatment. Transfusions should be scheduled regularly to help patients with bone marrow failure to maintain as normal a quality of life as possible. A patient should be transfused to maintain hemoglobin levels at a minimum of approximately 7-8 61 Fanconi Anemia: Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management g/dL so that the patient will be asymptomatic for his or her activity level. A post-transfusion hemoglobin level of 10-12 g/dL is generally sufficient to allow for normal activity, growth, and development in children, with a 3- to 4-week interval between transfusions. Irradiated blood products should be used to avoid transfusionassociated graft-versus-host disease. Iron also targets endocrine organs such as the pituitary, pancreas, thyroid, and parathyroid. Ferritin levels may be useful to monitor trends in total body iron over time but quantitative measurement of hepatic and cardiac iron burden are essential. However, a liver biopsy is the only technique that can determine the degree of hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis. Liver iron concentrations between 7-15 mg/g dry weight are associated with an elevated risk of iron toxicity. A liver iron concentration of greater than 15 mg/g dry weight is associated with a high risk of cardiac toxicity (45). As a general guide, chelation therapy should begin when the total volume of red cells transfused reaches 200 mL/kg (which roughly corresponds to a total of 12-18 red cell transfusions) or the liver iron concentration reaches 3-7 mg/g dry weight. The target liver iron concentration level is typically between 3-7 mg iron/g dry weight but many experts prefer levels less than 3 mg iron/g dry weight. Although generally effective, its use is complicated by the need for subcutaneous or intravenous injection. Subcutaneous infusions pose a risk of bleeding or infection in patients with thrombocytopenia or neutropenia. Patients who develop a fever should immediately cease deferoxamine therapy and undergo medical evaluation. The optimal dose of deferasirox is between 20-40 mg/kg, which can maintain iron balance in most patients, but unlike deferoxamine, may not be sufficient to reduce iron overload. However, the utility of deferiprone is limited by its side effects, which include neutropenia and fatal agranulocytosis, a particular concern in individuals with bone marrow failure, and arthralgias and arthritis. A small pilot study found that deferoxamine in combination with deferasirox was efficacious in individuals with severe iron overload. Cases of iron overload that are significant enough to warrant such aggressive treatments should be discussed with an expert who is familiar with combination therapy. As noted above, a long trial of oxymetholone or danazol (up to 6 months) is required before treatment is considered unsuccessful due to the lack of a platelet response or unacceptable side effects. Platelet transfusion is indicated in patients with severe bruising or bleeding, or who are undergoing invasive procedures.
Study participants were treated for 18 months and adverse events were assessed at the end of treatment diabetes medications bladder cancer buy glimepiride 2 mg without a prescription. Although this study did not meet inclusion criteria for this report with respect to population characteristics (the study did not involve allergic rhinitis or urticaria) diabetes definition gcse glimepiride 4 mg buy with amex, it was included in this paper because it provided long-term data on the safety of cetirizine in a large population of young children blood sugar magik zip purchase 2 mg glimepiride. Serious adverse events attributed to the study medication occurred in 1 child receiving cetirizine and 5 children receiving placebo diabetes insipidus blood osmolality generic glimepiride 2 mg visa. There were 10 accidental overdoses of study medications by study participants; 2 of these participants were receiving cetirizine. Symptoms and events (Evidence Table 22) were reported with similar frequency in cetirizine- and placebotreated groups. Age-appropriate increases in height and weight were observed during the study period. Antihistamines Page 30 of 72 Final Report Update 2 Drug Effectiveness Review Project Key Question 3. Are there subgroups of patients based on demographics (age, racial groups, gender), concomitant medications (drug-drug interactions), comorbidities (drug-disease interactions or pregnancy), for which one newer antihistamine is more effective or associated with fewer harms? Patients with allergic rhinitis with mild intermittent asthma or atopic dermatitis tolerated newer antihistamines similar to patients without these comorbidities. There was minimal increased risk of birth defects observed with H-1 receptor antagonists including cetirizine, fexofenadine, and loratadine. Detailed assessment Age, gender, race/ethnicity No direct evidence was available to determine whether any antihistamine has an advantage in efficacy or harms for any gender or racial group. Asthma Three fair-quality placebo-controlled trials were identified in patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma (Evidence table 24). Berger and colleagues139 examined desloratadine in patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis and asthma and found a significant decrease in total asthma symptom scores in the treatment group. There were no significantly different adverse events reported in primarily adult patients with allergic rhinitis and asthma compared with patients without asthma. There were no reports of worsening asthma with active treatment; only 2 placebo-treated patients146 reported asthma aggravated. Most patients included in these studies had mild intermittent asthma and were likely not using inhaled corticosteroids. Two trials evaluated cetirizine,159, 160 levocetirizine (Evidence Table 3),68, 146 and azelastine nasal spray (Evidence Table 1). Nasal burning, bitter taste or altered taste, and epistaxis were observed more often in azelastine-treated patients than with placebo. Atopic dermatitis An 18-month, placebo-controlled trial studied levocetirizine in 510 children 12 to 24 months in age who had atopic dermatitis, allergy to grass pollen or house dust mites, and family history of allergies. Antihistamines Page 31 of 72 Final Report Update 2 Drug Effectiveness Review Project About 96% of enrolled children reported at least 1 adverse event during the trial. The most commonly reported event was upper respiratory tract infections (levocetirizine, ~51% compared with placebo, ~50%). Worsening atopic dermatitis was low and occurred similarly between groups (levocetirizine, ~5% compared with placebo, ~6%). Febrile convulsions, however, were reported more often in levocetirizine-treated children than placebo (2. Although the investigators suspected the convulsions were not study medication-related, they could not rule out the possibility and recommend that this be explored further. There was one 30-month-old child that developed lymphadenopathy and was diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. The investigators judged that a relationship of study drug and this occurrence was unlikely. Pregnancy Rhinitis is one of the most common conditions during pregnancy, affecting more than 20% of pregnant women. We identified 1 additional cohort study (N=1882) that evaluated cetirizine exposure in the first trimester of pregnant women. Results from a systematic review with meta-analysis,121 a nested case-control study,127 and data from the National Birth Defects Prevention Study,167 indicated that loratadine exposure during pregnancy does not significantly increase risk of hypospadias in male infants.
References
- Kennedy WA 2nd, Hensle TW, Giella J, et al: Potassium thiophosphate laser treatment of genitourinary hemangioma in the pediatric population, J Urol 150:950n952, 1993.
- Donohue JP, Leviovitch I, Foster RS, et al: Integration of surgery and systemic therapy: results and principles of integration, Semin Urol Oncol 16(2):65n71, 1998.
- Kumagai K, Fukuda K, Wakayama Y, et al. Electrocardiographic characteristics of the variants of idiopathic left ventricular outflow tract ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2008;19(5):495-501.
- GAVALDA J et al: Brief communication: Treatment of Enterococcus faecalis endocarditis with ampicillin plus ceftriaxone. Ann Intern Med 146:574, 2007.
- Trnka L, Dankova D, Svandova E. Six years' experience with the discontinuation of BCG vaccination. 4.
- Choi J, Kim SG, Im JP, et al. Comparison of endoscopic ultrasonography and conventional endoscopy for prediction of depth of tumor invasion in early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2010;42:705-713.
- Sekharan J, Dennis JW, Veldenz HC, et al. Continued experience with physical examination alone for evaluation and management of penetrating zone 2 neck injuries: results of 145 cases. J Vasc Surg. 2000;32(3):483-489.