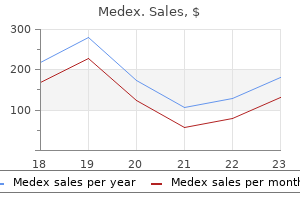
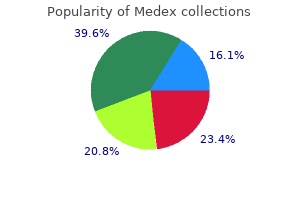
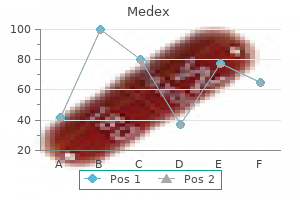
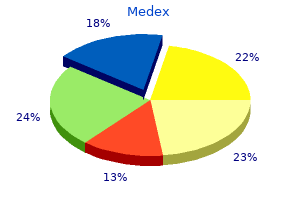
Medex
Michael K. Cahalan, MD
- Professor and Chair of Anesthesiology
- University of Utah School of Medicine
- Salt Lake City, Utah
In severe poisoning there may be gastrointestinal haemorrhage hiv infection rate san diego , hypotension lemon antiviral , drowsiness antiviral yiyecekler , convulsions and metabolic acidosis hiv infection gp120 . Gastrointestinal features usually appear in the first 6 hours and a patient who has remained asymptomatic for this time probably does not require antidote treatment. Activated charcoal does not bind to iron salts; therefore consider giving a gastric lavage if potentially toxic amounts of iron were taken. Try to make the patient vomit if other medicines or poisons have been taken by stimulating the back of the throat. Take the patient to a health facility as soon as possible, together with information about the substance concerned such as container, label, sample of tablets, berries etc. Symptoms: Most bites and stings result in pain, swelling, redness, and itching to the affected area. Treatment and Management Treatment depends on the type of reaction Clean the area with soap and water to remove contaminated particles left behind by some insects Refrain from scratching because this may cause the skin to break down and results to an infection Treat itching at the site of the bite with antihistamine Give appropriate analgesics Where there is an anaphylactic reaction treat according to guideline. Diagnosis of Scorpion poisoning (envenoming) Signs of envenoming can develop within minutes and are due to autonomic nervous system activation. Hospital care Antivenom o If signs of severe envenoming give scorpion antivenom, if available (as above for snake antivenom infusion). Clinical condition depends on the type of snake bite and amount of poison (venom) injected. Hence envenomation (poisoning) will be neurotoxic in cobra and mambas and sea snakes and haemotoxic in vipers and boomslang. Snake bite should be considered in any severe pain or swelling of a limb or in any unexplained illness presenting with bleeding or abnormal neurological signs. Contact with snakes, scorpions and other insects result in two types of injuries: those due to direct effect of venom on victim and those due to indirect effect of poison. Diagnosis of snake poisoning (envenoming) General signs include shock, vomiting and headache. These include: Shock Local swelling that may gradually extend up the bitten limb Bleeding: external from gums, wounds or sores; internal especially intracranial Signs of neurotoxicity: respiratory arrest or paralysis, ptosis, bulbar palsy (difficulty swallowing and talking), limb weakness o Signs of muscle breakdown: muscle pains and black urine Check haemoglobin (where possible, blood clotting should be assessed). If the bite was likely to have come from a snake with neurotoxic venom, apply a firm bandage to the affected limb from fingers or toes to proximal of site of bite; Clean the site with clean water to remove any poison and remove any fangs; If any of the above signs, transport to hospital which has antivenom as soon as possible. Treatment Hospital care Treatment of shock/respiratory arrest Treat shock, if present. Paralysis of respiratory muscles can last for days and requires intubation and mechanical ventilation or manual ventilation (with a mask or endotracheal tube and bag) by relays of staff and/or relatives until respiratory function returns. Give more slowly initially and monitor closely for anaphylaxis or other serious adverse reactions. If itching/urticarial rash, restlessness, fever, cough or difficult breathing develop, then stop antivenom and give Epinephrine 0. Response of abnormal neurological signs to antivenom is more variable and depends on type of venom. Anticholinesterases can reverse neurological signs in some species of snake (see standard textbooks of medicine for further details). Other treatment Surgical opinion Seek surgical opinion if there is severe swelling in a limb, it is pulseless or painful or there is local necrosis. Provide adequate pain relief Elevate limb if swollen Give antitetanus prophylaxis Antibiotic treatment is not required unless there is tissue necrosis at wound site Monitor very closely immediately after admission, then hourly for at least 24 hours as envenoming can develop rapidly. In general, venomous spider bites can be painful but rarely result in systemic envenoming. The dose of antivenom to jellyfish and spiders should be determined by the amount of the venom injected. Higher doses are required for multiple bites, severe symptoms or delayed presentation. The digestive tract is the part of our body that allows absorption of what we eat into our internal environment. The digestive tract is a long tube that starts in the esophagus and ends in the colon and rectum. Once food is eaten, the digestive system releases enzymes to break down food into small particles so they can be absorbed by intestinal mucosa. The tight junctions between intestinal mucosal cells allow only the absorption of tiny particles that the underlying intestinal immune system does not react against.
By supporting data-driven decisions symptoms of hiv infection in toddlers , Cortellis helps pharmaceutical companies antiviral used for cold sores , biotech and medical device/diagnostic firms accelerate innovation hiv infection blood transfusions . Republication or redistribution of Clarivate Analytics content hiv infection rate zimbabwe , including by framing or similar means, is prohibited without the prior written consent of Clarivate Analytics. Cortellis and its logo, as well as all other trademarks used herein are trademarks of their respective owners and used under license. When the lining becomes inflamed, the tendon cannot glide smoothly in its covering (sheath). The biceps tendon is one of the anchor points of the biceps muscle, which is important for bending the elbow and rotating the wrist. There is a slight pull of the tendon without obvious tendon tearing (it is microscopic tendon tearing). There is tearing of tendon fibers within the substance of the tendon or at the bone-tendon junction or muscletendon junction. The length of the tendon or whole muscle-tendon-bone unit is increased, and strength is usually decreased. Crepitation (a crackling sound) when the tendon or shoulder is moved or touched Causes Strain from sudden increase in amount or intensity of activity Direct blow or injury to the shoulder More likely with repeated injury to the biceps muscle-tendon unit In association with rotator cuff injury or inflammation, or other shoulder problems Risk Increases With Sports that involve contact, as well as throwing sports, gymnastics, weightlifting, and bodybuilding Heavy labor Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) Inadequate warm-up before practice or play Preventive Measures Common Signs and Symptoms Pain, tenderness, swelling, warmth, or redness over the front of the shoulder Pain that is worse with shoulder and elbow motion and function against resistance Limited motion of the shoulder or elbow Appropriately warm up and stretch before practice or competition. Maintain appropriate conditioning: o Shoulder and elbow flexibility o Muscle strength and endurance o Cardiovascular fitness Use proper technique. Take these as conservative treatment and resting of the directed by your physician. HealingPhone: (316) 838-2020 is usually quicker if caused by a direct blow (versus overuse). Possible Complications Prolonged healing time if not appropriately treated or if not given adequate time to heal Chronically inflamed tendon causing persistent pain with activity that may progress to constant pain (with or without activity), restriction of motion of the tendon within the sheath (adhesive or constrictive tenosynovitis), and potentially rupture of the tendon Recurrence of symptoms, especially if activity is resumed too soon or with overuse, a direct blow, or use of poor technique your physician immediately if any bleeding, stomach upset, or signs of an allergic reaction occur. Cortisone injections reduce inflammation, and anesthetics temporarily relieve pain. However, these are used only in extreme cases; there is a limit to the number of times cortisone may be given because it may weaken muscle and tendon tissue. Heat and Cold General Treatment Considerations Initial treatment consists of medication and ice to relieve the pain, stretching and strengthening exercises, and modification of the activity that initially caused the problem. These all can be carried out at home, although referral to a physical therapist or athletic trainer may be recommended. An injection of cortisone to the area around the tendon (within the sheath) may be recommended. Surgery to remove the inflamed tendon lining or to detach the degenerated tendon and re-insert it into the arm bone is not usually necessary and is generally only considered after at least 6 months of conservative treatment. Surgery to correct other shoulder problems that may be contributing to tendinitis may be recommended before surgery for the tendinitis itself. Cold should be applied for 10 to 15 minutes every 2 to 3 hours for inflammation and pain and immediately after any activity that aggravates your symptoms. Heat may be used before performing stretching and strengthening activities prescribed by your physician, physical therapist, or athletic trainer. Notify Our Office If Medication Symptoms get worse or do not improve in 2 weeks despite treatment New, unexplained symptoms develop (drugs used in treatment may produce side effects) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, such as aspirin and Dr. Grasp the bottom of a stick, handle of an umbrella, or blade of a golf club in your hand as shown. Using the stick, raise your arm overhead as shown until you feel a gentle stretch. Lie on your back holding a stick in both hands, keeping your hands shoulder-width apart. While standing near a wall as shown, slowly "walk" your fingers up the wall until you feel a gentle stretch. Lie on your back holding a stick, umbrella handle, or golf club in your hand as shown. Using the stick, slowly push your arm away from your side and as far overhead as you can without pain. Drape a towel over your opposite shoulder and grasp it with the hand that is behind your back.
If your child will be tested hiv infection how early symptoms , remember to call your health care provider before you go to the clinic hiv infection from mosquitoes . Keep in mind that some community testing sites will not test children under a certain age antiviral nclex questions . Contact your healthcare provider and the local health department if your child becomes sick hiv infection and blood type . While a child is ill, child care should be provided in the home by household members as much as possible. Encourage good habits: frequent handwashing, covering coughs and sneezes, use of face coverings in public (if over age 2), and staying home as much as possible. In the meantime, if you have any questions, please call [insert full name and position] at [phone #]. Your child can return to child care on [release from isolation date] as long as their symptoms have improved (gotten better), and they have not had a fever for 24 hours prior to the listed date. Your child can be tested at your regular health care provider, a local clinic, or a community testing site. To prevent spread to others in the child care facility, please keep all children in your household home and do not send them to child care or to in-person school until [release from household contact quarantine date]. Self-quarantine includes staying home from work, leaving the house only when necessary, wearing a mask in public, washing hands frequently, not having visitors, not sharing utensils, towels or other personal items, and staying 6 feet from others in your home as much as possible. Monitor yourself and the others in your household for symptoms and see a doctor if you become sick. We realize the burden this may place on your family, but we want to do what is best to keep you, your family, and others at the child care facility safe and well. If anyone in your household has needs that cannot be met during this isolation and self-quarantine period, please reach out to your local health department for guidance. The table can be used as a checklist for routine cleaning or as a checklist for completing a "deep clean. Employees can initial in the "Completed" column to indicate a task has been completed. A "deep clean" is simply the completion of all tasks on a routine cleaning schedule, but completed all in the same 1-2 day period, rather than according to their routine weekly or monthly schedule. If not possible, vacuum daily when Upholstered furniture children are not present. If washing by hand, use sanitizer safe for food contact as final step in process; use of automated dishwasher will sanitize. Recommend cleaning and sanitizing multiple times a day, as these are high touch items/areas. If no equipment guidance, use alcohol-based wipes containing at least 70% alcohol; (tablets, touch dry thoroughly. Disinfect: To destroy or inactivate most germs on any inanimate object, but not bacterial spores. Unexpired household bleach will be effective against coronavirus when properly diluted. Do not use a bleach product if the percentage is not in this range or is not specified. Part 2 Has your child developed any of the following symptoms within the last 24 hours? Questions should be posed to parents of small children; children old enough to understand and answer for themselves may be asked directly. Fever, vomiting, and diarrhea-alone or together-should exclude a child from child care. Child may remain at facility Child should wash (or sanitize) hands before having contact with other children or staff/caregivers. Staff member may remain at facility Staff member should wash (or sanitize) hands before having contact with children or other staff/caregivers.
High-pitched tinkling sounds or rushes are usually associated with an obstructive process antiviral imdb . As the examiner continues to listen over the entire anterior abdomen hiv infection latency , the pressure on the head of the stethoscope increases until the examiner is hiv infection after 5 years , in fact antiviral products , palpating with the stethoscope. Palpation is begun as far away from the area of pain identified by the child as possible. Directing fingers into the abdomen (perpendicular) as a method of palpation is unnecessary and often frightening. Some children are extremely stoic, and only the slightest grimace betrays the discomfort they are experiencing. Guarding refers to the voluntary or involuntary (often referred to as rigidity) contraction of the abdominal musculature. Fear of pain, rather than actual pain elicited by palpation, is the most common cause for voluntary guarding while involuntary guarding results from reflexive spasms of the abdominal musculature in the setting of peritoneal irritation. When encountering tenderness, the examiner should palpate only deeply enough to elicit the complaint of pain and some guarding. The standard method to elicit rebound is to palpate deeply, then suddenly remove the palpating hand. Although this sign aids in the determination of the presence of an intraperitoneal inflammatory process, it is not necessary to cause extra discomfort or stress, particularly in younger children; it is not recommended. Peritoneal irritation can also be detected by maneuvers such as asking the child to jump, cough, or tapping the feet while observing for facial signs of discomfort. An inflammatory mass, such as an inflamed appendix, a psoas abscess, or a perinephric abscess, in contact with the psoas muscle is the cause of this pain. This sign results from contact of an inflammatory mass with the obturator muscle. Percussion at the costovertebral angle elicits pain in the presence of renal or perinephric inflammation. If a more thorough examination or an intravaginal examination is needed in prepubertal girls, it should generally be performed with the patient under anesthesia. If an imaging study or colonoscopy is planned, a rectal examination may be unnecessary. If constipation is suspected as the cause for pain, rectal examination should be performed but should be the last part of the physical examination and should be performed only once. The child should be relaxed and should be given an honest explanation of the procedure. The examiner should use plenty of lubricant and should perform the rectal examination very gently. Overreliance on the complete blood count alone can cause delay in reaching the correct diagnosis. Urinalysis the urinalysis is an important and useful laboratory test in the evaluation of abdominal pain. The presence of ketones and a high specific gravity suggest poor food intake and dehydration. A pregnancy test should be performed on postpubertal girls, regardless of sexual activity history. Complete Blood Cell Count the hemoglobin and hematocrit levels can reveal anemia caused by acute or chronic blood loss (as with ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease, Meckel diverticula) or the anemia of chronic disease (as with systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease). In uncomplicated acute appendicitis, the white blood cell count ranges from normal values to as high as 16,000. A very high white blood cell count (>18,000/mm3) indicates intestinal gangrene, perforation, peritonitis, or abscess formation, but this count may also be high in acute bacterial gastroenteritis, streptococcal diseases, pyelonephritis, pelvic inflammatory disease, hemolytic uremic syndrome, and pneumonia. Imaging Evaluation Multitudes of imaging studies are available; none should be obtained until the patient has been examined. Only approximately 10% of abdominal radiographic studies are positive when they are obtained as part of the routine work-up for abdominal pain. In acute appendicitis, a calcified appendicolith (appendiceal fecalith) may be seen.
. Preventing an HIV infection | Infectious diseases | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy.
References
- Gupta A, Rhodes GJ, Berg DT, et al. Activated protein C ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury and downregulates renal INOS and angiotensin 2.
- Witting JI, Bourdon P, Brezniak DV, et al: Thrombin-specific inhibition by slow cleavage of hirulog-1.
- Park JH, Qiao B, Panageas KS, et al. Early death rate in acute promyelocytic leukemia remains high despite alltrans retinoic acid. Blood 2011;118(5):1248-1254.
- Saperston, K., Smith, J., Putman, S. et al. Endoscopic subureteral injection is not less expensive than outpatient open reimplantation for unilateral vesicoureteral reflux. J Urol 2008;180 (Suppl 4):1626-1629; discussion 1629-1630.
- Collins J, Bove KE, Dimmock D, Morehart P, Wong LJ, Wong B. Progressive myofiber loss with extensive fibro-fatty replacement in a child with mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome and novel thymidine kinase 2 gene mutations. Neuromuscul Disord. 2009;19(11):784-787.
- Lichstein E, Ribas-Meneclier C, Gupta PK, et al. Incidence and description of accelerated ventricular rhythm complicating acute myocardial infarction. Am J Med. 1975;58:192.
- Cervellione RM, Mantovani A, Gearhart J, et al: Prospective study on the incidence of bladder/cloacal exstrophy and epispadias in Europe, J Pediatr Urol 11(6):337.e331n337.e336, 2015.
- Chieffo A, Morici N, Maisano F, et al. Percutaneous treatment with drug-eluting stent implantation versus bypass surgery for unprotected left main stenosis: a single-center experience. Circulation. 2006;113:2542-7.