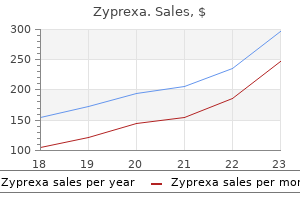
Zyprexa
Eloise J. Prijoles, M.D.
- Greenwood Genetic Center
- Columbia, South Carolina
In ancient sophisticated cultures medicine 93 2264 5 mg zyprexa order overnight delivery, magical beliefs were connected directly to punishment as a result of insulting the gods treatment sciatica zyprexa 2.5 mg sale. The perception of pain as "punishment by God" within the framework of religious structures is still widespread today; for example medications dialyzed out 2.5 mg zyprexa order with amex, pain patients feel "less desire to reduce pain and feel more abandoned by God" [14] 5 medications purchase 5 mg zyprexa amex. Lovering [7] investigated cultural beliefs with regard to causes of pain in various cultures and reports of references by the patients to "the evil eye" (Filipino, Saudi, and Asian cultures) or the power of the ancestors (Tswana culture). The consideration of subjective assumptions with regard to the development of pain- such as belief in magical, biomedical, or biopsychosocial approaches to pain-make it possible to develop relevant therapy concepts by incorporating the wishes and targets of patients. Within the theoretical understanding of pain, classical conditioning according to Pavlov, based on stimulus and reaction, builds the foundation for further considerations. The feeling of pain is primarily a reaction to a pain stimulus and thus has a response. In this regard, a primarily neutral stimulus, for example, a rotation of the body with evidence of relevant muscular malfunction, is connected to feeling an unpleasant psychophysiological reaction such as increased heart rate or a painful increase of tension in muscles. The consequence is to avoid this type of rotation of the body, which can make sense when the pain is felt for the first time. However, if this behavior is maintained, an increase in the muscular malfunction leads to a strengthening of the mechanism. If both stimuli are often experienced together, then the body reacts to the original neutral stimulus. For example, stress stimuli, which are often accompanied by pain, can be the cause of subsequent pain. In this paradigm, it is hypothesized that behavior increases in frequency if reinforced. The longer pain persists, the greater the likelihood that the pain experience is primarily influenced by reactions to the environment. Behavioral attitudes will more than likely emerge when they are directly positively strengthened or when negative effects can be avoided. The awareness of pain can thus be affected by positive strengthening, for example, by increased care and attention by third parties. A negative strengthening of pain awareness can be caused by the absence of unpleasant activities or by avoidance of conflicts as a result of expressing pain. This behavior can be sustained even after alleviation of pain and thereby lead to a renewed sustainment of the vicious cycle, for example, by sustained avoidance of beneficial behavior such as activity. The chief purpose of psychological assessment is to get a complete picture of the pain syndrome with all affected dimensions: somatic, affective, cognitive, behavioral, and above all, the individual consequences for the patient. The complete information and the analysis of conditions of pain maintenance enable us to fix targets for treatment. For example, a patient with a diagnosis of back pain and avoidance behavior needs education to understand why it makes sense to minimize such behavior. A patient with back pain, avoidance behavior, and depressive reactions needs a good explanation of the biopsychosocial model. A better understanding can enable the patient to develop better strategies of coping and minimize helplessness. What are psychological models for explaining conditions of pain development and maintenance? Cognitive and behavioral factors, as well as classical conditioning, are factors we have to think about in this Psychological Evaluation of the Patient with Chronic Pain 97 Coping with pain includes all attempts made by a person to influence the pain, whether by thought or deed. Adaptive behavioral strategies include: "After my work is done, I will take a short break, and after that I can do something I want to do," or "After a little walk in the sun I will feel better. For example: `It is better to do the work of the day in short periods of time and have a little rest, rather than to do all the work in two hours and have to rest for the remainder of the day. Patients in Scotland reported as the main issue the prospect of death, saying that suffering of pain is unusual and spiritual needs are evident. In comparison, patients in Kenya reported physical suffering as the main issue, especially as analgesic drugs are unaffordable.
Chronic scrotal pain is a complication of hernia repair medications you can buy in mexico generic zyprexa 2.5 mg buy on-line, but in trials treatment kennel cough cheap zyprexa 2.5 mg online, it is seldom reported or it is put under the term chronic pain (not specified) medications descriptions cheap zyprexa 5 mg mastercard. In almost all studies medicine lodge treaty cheap 7.5 mg zyprexa amex, the frequency of scrotal pain was significantly higher in the laparoscopic than in the open group (4,11-13). In one particular study, there was no difference at 1 year but after 5 years, the open group had far fewer patients with scrotal pain (14). The best known referred pain is of myofascial origin, especially the trigger points (see Chapter 9). Problems inside the bladder or abdominal cavity can also give rise to pain in the scrotal area. When making a treatment plan for patients with scrotal pain, it is important to remember this phenomenon. Gentle palpation of each component of the scrotum is performed to search for masses and painful spots. A rectal examination is done to look for prostate abnormalities and to examine the pelvic floor muscles. In > 80% of patients, ultrasound does not show abnormalities that have clinical implications (15,16). If physical examination is normal, ultrasound can be performed to reassure the patient that there is no pathology that needs therapy (mainly surgery). Ultrasound can be used to diagnose hydroceles, spermatoceles, cysts and varicoceles. When abnormalities such as cysts are seen, this may play a role in therapeutic decision making. In general practice, it seems that many urologists are performing ultrasound examination in almost all patients. It is becoming increasingly clear that advances in the non-surgical management of testicular pain are mainly based on the emergence of pain relief as a specialty. Knowing this, it seems obvious that referring to a multidisciplinary pain team or pain centre should be considered in an early phase of the consultation (18). The pelvic floor muscles should be tested and will often be found overactive, which means that they contract when relaxation is needed. More specific myofascial trigger points are found in the pelvic floor, but also in the lower abdominal musculature. Treatment consists of applying pressure to the trigger point and stretching the muscle (22,23) (see Chapter 9). In the literature, there is consensus on postponing surgery until there is no other option. All the studies that have been done were cohort studies but their success rates were high. The size of effect was so remarkable that it is recommended that randomised studies are performed to obtain better proof. The three cohort studies that are found were consistent in the indication criteria, the diagnostic methods applied, and the surgical approach used. They included patients with chronic scrotal pain who did not respond to conservative treatment. Ultrasound showed no abnormalities and a spermatic cord block showed pain relief of > 50%. The cord is transected in such a way that all identifiable arterial structures, including testicular, cremasteric, deferential arteries and lymphatic vessels are left intact. The complication of testicular atrophy was seen in 3-7% of the operated patients (24-26). The laparoscopic route for denervation seems feasible but the results are unclear (27). Epididymectomy shows the best results in patients with pain after vasectomy, or pain on palpation of the epididymis and when ultrasound shows multiple cysts. These results are also from cohort studies but the fact that assessment can help in predicting the chance of success makes further studies worthwhile. One study in our search has yielded different results, namely, that post-vasectomy patients fared worse and that ultrasound did not help in predicting the result of the operation. There have been no studies than can help in making a rational decision on whether to perform orchiectomy.
Purchase zyprexa 5 mg online. FRED MIKA Withdrawal Symptoms part 1.
Implanted catheters need highly specialized care and tend to fail frequently treatment rheumatoid arthritis discount 2.5 mg zyprexa visa, and therefore they are indicated only in very special circumstances medicines360 zyprexa 10 mg buy on line. With a small and simple device medicine 5852 zyprexa 10 mg line, an electrical current is applied to skin areas with a certain current and frequency treatment croup 2.5 mg zyprexa buy otc, producing a nonpainful dysesthesia. With this treatment, the patient may have short-term or even long-term pain reduction. All these techniques are outside the scope of this manual because they are highly sophisticated, very expensive, and require lengthy experience in pain management. Another simpler option, which might be used by a therapist experienced in block techniques, most likely an anesthesiologist, is ablation of nerves. This treatment is effective for prolonged periods Maged El-Ansary of time but is not permanent. With careful use of the technique, the complication rate for this patient group can be acceptable. These will range from lack of sleep, joint stiffness, secondary infections, and vascular strokes up to suicide attempts. Thus, adequate diagnosis and treatment of acute herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia should be expected-and to a certain extent this is possible in most patients-from the caring physician or other health care worker. Mechanical allodynia in postherpetic neuralgia: evidence for central mechanisms depending on nociceptive C-fiber degeneration. Haanpдд M, Dastidar P, Weinberg A, Levin M, Miettinen A, Lapinlampi A, Laippala P, Nurmikko T. Gabapentin in postherpetic neuralgia: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study. Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings Chapter 25 Central Neuropathic Pain Maija Haanpдд and Aki Hietaharju Case report 1 Abdul Shamsuddin, a 35-year-old shopkeeper from Gulshan, Dhaka, was found by his wife lying on the floor of his apartment. He was brought into the hospital on a makeshift stretcher carried by four relatives, all saying different things about what had happened. In the emergency room, he was conscious but not able to move his legs or left arm. He was complaining of severe burning pain in his right hand and deep aching pain in both of his upper extremities. The man explained, incoherently, that his house had been entered by a gang of robbers, and the last thing he remembered was a loud gunshot. There was severe hyperesthesia, hyperalgesia, and dynamic allodynia as well as impaired cold sensation in the 4th and 5th fingers and on the ulnar side of his right hand. In the left hand, there was mild dynamic allodynia, and hyperalgesia was noticed in the 3rd finger. A radiograph of the cervical spine showed a posterior arch fracture of C7 and a 9-mm bullet lying close to the scapula on the right side. The continuity of the spinal cord was intact, and no signs of hematoma were present. This case shows that neurological injury and spinal cord pain can occur even if a projectile does not penetrate the spinal canal. Cord contusion was probably the result of the kinetic energy transmitted by the bullet. Within 4 years, the neuropathic pain started gradually to resolve, and gabapentin was successfully tapered off. Case report 2 Shabana, an Afghan housewife from Jalalabad in her late thirties, came to a psychiatric outpatient clinic escorted by her husband. She had suffered for more than 2 years from continuous burning pain in her left hand and the right side of her face. History taking revealed that she had had a sudden attack of vertigo, slurred speech, and motor weakness in her left extremities 3 years earlier. Most of her symptoms had subsided within 2 days, but the motor weakness had persisted for weeks. She reported that the painful symptoms had appeared about 2 months after this attack. Neurological examination revealed slight clumsiness and ataxia in her left arm, but muscle strength was regarded as normal. A conspicuous decrease in cold and pain sensibility was noticed on her right cheek, and in the lower two-thirds of her left arm as compared to the contralateral side. Due to 189 Guide to Pain Management in Low-Resource Settings, edited by Andreas Kopf and Nilesh B.
The muscles of the pharynx have been considered as individual muscles in all veterinary literature medications held before dialysis generic zyprexa 5 mg with visa. In Ruminantia treatment xeroderma pigmentosum effective 10 mg zyprexa, the Sulcus ventriculi is divided by the Ostium reticuloomasicum and Ostium omasoabomasicum into three segments: Sulcus reticuli medicine zantac buy zyprexa 5 mg without prescription, Sulcus omasi medications 4 times a day cheap zyprexa 10 mg amex, and Sulcus abomasi. In Ruminantia the forestomach or Proventriculus is divided into three parts: the Rumen, Reticulum, and Omasum. The term Ruminoreticulum is required by the morphological and physiological unity of the two compartments. It forms, in conjunction with the free borders of the Laminae omasi, the Canalis omasi. This is the part of the Sulcus ventriculi along the interior surface of the Curvatura minor abomasi. This is defined in veterinary anatomical literature as the short terminal part of the small intestine to which the Plica ileocecalis is attached. Although the part of the Basis ceci cranial to the Papilla ilealis develops from the first part of the embryonic colon, it is conventionally included in the Basis ceci. An Ampulla hepatopancreatica is formed at the orifices of the bile and pancreatic ducts in the cat and horse. In the sheep and goat the bile and pancreatic ducts unite before they reach the duodenum. Although it is not independent of the duodenal musculature as it is in man, a tract of muscle fibers passes around the ampulla in the cat, or the common hepatopancreatic duct in the sheep and goat, or the terminal part of both ducts in the dog and horse. This structure in domestic mammals is not homologous to the superior concha of man. The horse has two maxillary sinuses on each side, each with its own nasomaxillary opening. This "butterfly cartilage" on the dorsal surface of the arytenoid cartilages in Carnivora is not homologous to the human sesamoid cartilages. The muscle layer of the Bronchi in domestic mammals lies between the Lamina propria and the Tela submucosa. Inclusion of the basal border with the ventral border eliminates an important clinical distinction. The terminology of the lung in domestic mammals is best derived from the shape of the lung - a semicone with an apex and an oblique base. The criterion for naming the lobes is the division of the bronchi rather than external fissures. All species of domestic mammals have a cranial lobe and a caudal lobe on both lungs, and an accessory lobe on the right lung. In all species except the horse, the cranial lobe of the left lung is divided into cranial and caudal parts by an intralobar fissure. In Ruminantia the right cranial lobe is also divided into cranial and caudal parts. This is the recess of the right pleural cavity between the caudal mediastinum proper and the Plica venae cavae. In Carnivora, sheep, goat, and horse the Papillae renales are fused to form a Crista renalis. Textbook usage does not include the Calices in the Pelvis, which is only the dilatation at the end of the ureter. These tubular diverticula of the equine renal pelvis extend into the cranial and caudal ends of the kidney. Because the dorsal wall of the bladder does not form a Fundus vesicae in domestic mammals, this N. The first term designates the elevation of the mucosa produced by the ureter in its course in the wall of the bladder. In veterinary anatomy, the Plica ureterica is the lateral boundary of the Trigonum vesicae. In Ruminantia, Margo epididymalis is medial, Margo liber is lateral, and the surfaces corresponding to Facies lateralis and medialis of other species are caudal and cranial. It is the peritoneal fold that suspends the fetal testis from the dorsal abdominal wall, and contains the testicular vessels and nerves.
References
- Mauriello A, Sangiorgi G, Fratoni S, et al: Diffuse and active inflammation occurs in both vulnerable and stable plaques of the entire coronary tree: A histopathologic study of patients dying of acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;45:1585-1593.
- Sun L, Wang D, Zubovits JT, Yaffe MJ, Clarke GM. An improved processing method for breast whole-mount serial sections for three-dimensional histopathology imaging. Am J Clin Pathol. 2009;131(3):383-392.
- Takis C, Saver JL. Cerebrovascular Disease. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1997.
- Tang DC, Prauner R, Lui W, et al. Polymorphisms within the angiotensinogen gene (GT-repeat) and the risk of stroke in pediatric patients with sickle cell disease: A case-control study. Am J Hematol 2001;68:164-9.