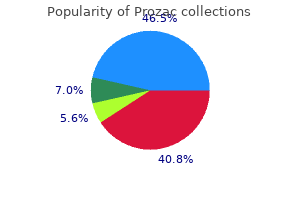
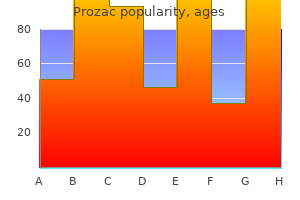
Prozac
Benjamin O. Anderson, MD
- Director, Breast Health Clinic
- Professor of Surgery and Global Health-Medicine
- Department of Surgery
- University of Washington
- Seattle, Washington
Check cholesterol and kidney function once a year and screen for diabetes every 2 years depression symptoms how long . Newer antiplatelet drugs like clopidogrel are more expensive and only a little more effective depression test for disability . Advise to walk to the point of pain and a little beyond to encourage new blood supply depression fracture . Brain scans diagnose the type of stroke but are not widely available and are very expensive depression symptoms not showering . After strokes, a person needs intensive physiotherapy provided by the hospital staff and family to prevent contractures and pressure sores and to promote re-education and rehabilitation. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal tonsillitis. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints and a characteristic but uncommon rash. Treating people who have strep throat with antibiotics, such as penicillin, decreases their risk of getting rheumatic fever. Give benzathine penicillin (or erythromycin if allergic to penicillin): Adult and child > 30kg give 900mg (1. If a patient presents with a cough and green or yellow sputum, with or without fever, but without fast breathing, they may have acute bronchitis. Most mild cases of acute bronchitis will resolve without antibiotics and paracetamol can be given for fever and to reduce cough symptoms. If the person is coughing up a lot of yellow or green sputum, amoxicillin can be given. Asthma Asthma is a chronic disease of airways presenting with reversible airways from smooth muscle contraction. Symptoms are often worse at night, and may be triggered by the cold, by exercise, by other allergens like dust, by taking aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatories. If caused by an infection, there may be crepitations in one part of the chest with widespread wheeze across the rest of the chest. Severe exacerbations of asthma are very dangerous with high mortality if not treated quickly and effectively. Treat obesity/ malnutrition Increase medication if often breathless Look for anxiety/ depression as breathlessness is frightening. Hospital and Referral Health Centre Guidelines 145 Step 4 Step 5 Check inhaler use & technique. In adults only: consider oral steroids or oral theophylline or oral salbutamol Adults: Beclometasone 1000mcg 2 x per day Child > 5 400mcg 2 x per day. Severe side effects of steroids: thin bones, weight gain, diabetes, gastric ulcer. In life threatening asthma when all the above has already been given, and no improvement with nebuliser, aminophylline may be needed. Antibiotics are not indicated unless there is clear evidence of infection (fever, productive cough, crepitations in the chest). Ensure person and parents know how to use inhaler and spacer, how to take oral prednisolone and know signs of exacerbation and when to return.
Some risk factors of developing a tinea versicolor infection include being in a warm depression symptoms unemployment , humid environment depression test ireland , immunosuppression depression unspecified icd 9 code , malnourishment depression treatment centers , high plasma cortisol levels, genetic predisposition, and poor skin hygiene. True/False: Oropharyngeal candidiasis and candidal diaper dermatitis often occur together because of C. Indicate whether the following agents are active against tinea, candida or both: a. Treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis and candidal diaper dermatitis in neonates and infants: review and reappraisal. In 57% of patients with oropharyngeal candidiasis, candidal diaper dermatitis is also seen (6). In darker skinned individuals they can appear as either hyperpigmented or hypopigmented macules. Sparks this is an 11 year old, previously healthy male who presents to the office with a chief complaint of extreme pain from a 3 day old puncture wound on his right calf. Over the next 36 hours, the skin near his wound progressively develops a bluish discoloration, blisters, and bullae. He continues to require daily surgical debridement until the sixth day of hospitalization, but he slowly improves. It is characterized by microbial spread along the fascial planes into deep tissue, which results in necrosis of the superficial tissue. For example, necrotizing cellulitis may involve the fascial planes secondarily or vice versa. The most common species of bacteria cultured from a study of 182 subjects in Maryland were Streptococcal species, Staphylococcal species, Enterococcal species, and Bacteroides species. The reason for this increase is unknown, but it may be related to the increasing incidence of other types of invasive streptococcal infections since 1985 (9). The M protein has been found responsible for protecting the bacteria from phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear leukocytes (10). Exotoxins recruit T cells and increase production of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1-beta, and interleukin 6. The effects are characterized by fever, shock, edema, and multiple organ failure (11). The differential diagnosis of severe pain and inflammation of the skin includes cellulitis, erysipelas, acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis, acute hemorrhagic edema of infancy, drug reactions, and vasculitis. However, cellulitis extends only to the subcutaneous tissue and is poorly demarcated. Definitive differentiation from necrotizing cellulitis is generally established with surgical incision and probing. Erysipelas is red, raised, well-demarcated areas of induration and usually involves only the superficial cutaneous tissue. It may begin as swelling and erythema around the umbilicus and progress to a purplish discoloration and periumbilical necrosis during the subsequent hours or days (13). In a study, almost 50% of pediatric cases were superimposed upon varicella in its 3rd-4th day of progression (8). The history frequently reveals a persistent fever after the third day of rash, associated with severe, localized pain, over an area of swelling, erythema, and possibly necrosing skin (14). However, physicians may consider recommending acetaminophen instead of ibuprofen for children with varicella (15). In the first 24-48 hours, it is associated with edema, erythema, and warmth of the skin overlying the necrotizing tissue. Its tenderness will also disappear as the superficial nerves experience ischemia (17). This progression is both faster and more severe than that seen in cellulitis or erysipelas (18). Therefore, the most important first steps of medical management are probably the gram stain and cultures of both the blood and the wound, if one is present. Contrast enhanced images may show asymmetric thickening of the deep fascia and/or gas bubbles in the deep tissue.
Childhood fever: correlation of diagnosis with temperature response to acetaminophen mood disorder nos 311 . Febrile core temperature is essential for optimal host defense in bacterial peritonitis depression symptoms nightmares . Some recent research in the field of neurotropic viruses with especial reference to lymphocytic choriomeningitis and herpes simplex anxiety zone pancreatic cancer . Effects of high ambient temperatures on various stages of rabies virus infection in mice depression anxiety test . Prognostic factors associated with improved outcome of E coli bacteremia in a Finnish University hospital. Community acquired pneumonia in the elderly: association between lack of fever and leukocytosis and mortality. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: a review of 28 cases with emphasis on improved survival and factors influencing prognosis. Adverse effects of aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen on immune function, viral shedding, and clinical status of rhinovirus infected volunteers. Invasive group A streptococcal infection and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug use among children with primary varicella. The first febrile seizure: antipyretic instruction plus either Phenobarbital or placebo to prevent recurrence. Effect of acetaminophen and of low intermittent doses of diazepam on prevention of recurrences of febrile seizures 1995:126:991-995. Antipyretic effectiveness of acetaminophen in febrile seizure ongoing prophylaxis vs sporadic usage. Risks for bacteremia and urinary tract infections in young febrile children with bronchiolitis. An orthopedic procedure is performed to drain some pus and to obtain a culture and biopsy. Cultures of his blood and the bone aspirate grow Staph aureus which is sensitive to cephalosporins and methicillin. His medical insurance company approves inpatient antibiotics for 7 days and requests that the remainder of his antibiotics be administered as an outpatient. Is there a rational method to provide him with inpatient levels of antibiotics as an outpatient? Each bacteria has a level of antibiotic which will inhibit growth but not kill the organisms. Pharmacologists have taught us that some antibiotics are "bactericidal" and some are "bacteriostatic". These terms are slight misnomers since all antibiotics are potentially bactericidal and bacteriostatic at different concentrations. The idea is that if cell wall formation is blocked, the organisms will lyse and perish, but if metabolism or protein synthesis is blocked, the organisms merely slow down. While this is true to some degree, bactericidal or bacteriostatic outcomes are dependent on the concentration of the antibiotic as well. A low dose of a "bactericidal" antibiotic may only inhibit bacterial growth, while a high dose of a "bacteriostatic" antibiotic will be bactericidal. Additionally, organisms which are not proliferating may not be significantly affected by anti-cell wall antibiotics, in which case antiribosomal antibiotics would be more effective. However, if one drowns the cockroach in bug spray (a cockroach-cidal level), the cockroach will perish. However, to understand this better, the following clinical example will be used to demonstrate these concepts. Refer to the table below: Page - 175 Tube 1 2 3 4 5 6 Antibiotic Concentration 10. There are six tubes with varying concentrations of antibiotic in a bacterial culture broth. Tube 1 contains the highest concentration of antibiotic and tube 6 contains the lowest concentration of antibiotic. After a 2 day incubation, the first 4 tubes are clear (which indicates that the organisms did not grow in these tubes). Tubes 5 and 6 are turbid due to bacterial growth which means that an antibiotic concentration of 0. For tubes 1, 2, 3 and 4, it is not known whether the organisms present in these tubes have died (bactericidal concentration) or their growth is merely inhibited (inhibitory concentration).
. MY EXPERIENCE WITH POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION | & NOW POSTPARTUM ANXIETY.
Diseases
- Weber Parkes syndrome
- Macrocephaly dominant type
- Muscular dystrophy congenital, merosin negative
- Mercury poisoning (Mercurialism)
- Tuberculosis
- Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens
- Thiele syndrome
- Vitamin E deficiency
- Pityriasis lichenoides chronica
- Ethylmalonic adipic aciduria
References
- Bensimon G, Lacomblez L, Meininger V. A controlled trial of riluzole in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1994; 330:585-591.
- Arnold R, Ley-Zaporozhan J, Ley S, et al. Outcome after mechanical aortic valve replacement in children and young adults. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:604-10.
- MacNee W. Pulmonary and systemic oxidant/antioxidant imbalance in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2005; 2: 50-60.
- McBeath, J. G., & Nanda, A. (2000). Roller coaster migraine: An underreported injury? Headache, 40(9), 745n747.
- Gabikian P, Clatterbuck RE, Gailloud P, et al: Developmental venous anomalies and sinus pericranii in the blue rubber-bleb nevus syndrome, case report, J Neurosurg 99:409-411, 2003.
- Dawson LA, Ten HRK. Partial volume tolerance of the liver to radiation. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2005;15(4):279-283.
- Teerijoki-Oksa T, Jaaskelainen SK, Forssell H, et al. Risk factors of nerve injury during a mandibular sagittal spit osteotomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002;31:33-39.