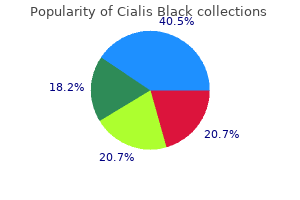
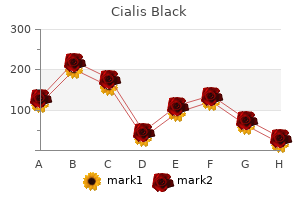
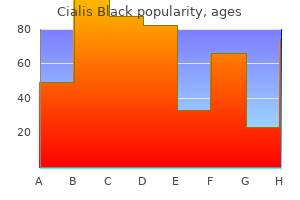
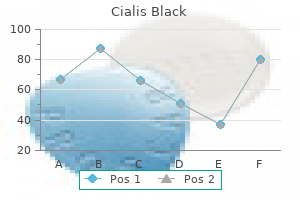
Cialis Black
Michael S. Lempel, DO
- Obstetrician/Gynecologist
- Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Potomac Hospital
- Woodbridge, Virginia
Microvascular and macrovascular complications cause morbidity erectile dysfunction latest treatments buy 800 mg cialis black, greater health-seeking and increased mortality risk in all regions of the world [23 impotence 20 years old cheap 800 mg cialis black with amex,27 erectile dysfunction treatment at home cheap cialis black 800 mg on-line,73] impotence hypnosis purchase 800 mg cialis black with mastercard. Health utilization patterns Health seeking and health utilization behaviors are influenced by a number of individual, provider and system level factors. In the case of diabetes, ill health and morbidity as well as preventative care motives result in incrementally more health service utilization. In Latin America, diabetes accounts for an estimated 35 million medical visits annually [74]. Although studies from most regions of the world report late-stage macrovascular or microvascular complications as the leading cause of diabetes-related hospitalizations, lower income settings such as Ethiopia confront a greater proportion (almost two-thirds) of admissions in the form of acute episodes of dysglycemia. Health care infrastructure and financing have strong impacts on health seeking and utilization. In India, estimates suggest that 8595% of all health care costs are borne by individuals and their families from household income [7881]. In Latin America, 40 60% of diabetes expenses are derived from out-of-pocket payments. A survey in Jamaica showed that 57% of the sample reported financial difficulties as a result of illness, and of these, half disclosed that they had avoided therapy because of economic constraints [74]. When one considers that the average number of medications used by people with diabetes in India is 3. These drugs include antihypertensives, lipid-lowering, antidepressant medications and aspirin in addition to glucose-lowering drugs). The use of oral hypoglycemics increases health expenditure by 40% compared to the general population, while regular insulin use is a further twofold greater expense. As such, data from Germany show that use of insulin the Global Burden of Diabetes Chapter 5 with or without oral agents increases total costs 3. Increased health seeking and utilization in people with diabetes and associated complications result in greater medical costs incurred, compared to the general non-diabetic population. Of those with any form of work disability inducing absence and/or poor productivity, over half had minor and/or major signs and symptoms of depression [92]. The complexity of disability as a limitation of individual and societal function is in quantifying this shortcoming. There are several methods that have been used which factor in age, education and occupation, but most have at least some imperfection because of the necessity of making judgments about the value of activities. This is especially difficult where there are cultural and ideological dissimilarities between the evaluator and the population being appraised. Disability Aside from the medical or biologic dysfunction caused by disease, there are implications of ill health for individual and interactive functioning in society. Excluding the medical aspects of diabetes-related complications that directly restrict bodily function, diabetes may be considered a "hidden" disability, whereby the individual concerned is hampered from routine activities, but displays no physical manifestation of this illness. For example, children with diabetes may be unable to participate in all activities their contemporaries are engaged in and may suffer wrongful discrimination. Adults in the workplace may have lower work performance by virtue of any number of symptoms (impaired fine motor skills and concentration, grogginess, urinary frequency) [85] or even decline in cognitive functioning [8688]. Those requiring insulin may be limited additionally by highly structured activities of daily living (the requirement of meticulous glucose monitoring, insulin administration, timed eating), recurrent hospitalizations, hyperglycemic and hypoglycemic episodes, and by regular preventative or therapeutic medical visits. Indeed, the physical manifestations of diabetes become more significant with the development of complications. As such, visual impairment, restricted mobility (from shortness of breath, chest pain or even amputation) and general ill health (ranging from increased susceptibility to infection all the way to uremia related to irreversible renal dysfunction) are all considerable impediments to productive work and engagement in socially valuable activity. Depending on the health status of the individual and severity of disease, disability can be temporary or permanent. There is limited country-specific data on the permanent disability resulting from diabetes, although diabetes is the leading cause of adultonset blindness, non-traumatic amputations and irreversible kidney failure worldwide [22]. Data from Chile showed that 8% of people with diabetes had some form of permanent disability [74].
Hyperglycemia interferes with the prokinetic effect of intravenous erythromycin on gastric emptying in healthy subjects and patients with diabetes [34] erectile dysfunction treatment boston medical group 800 mg cialis black with visa. Because both liquids and homogenized solids are more readily emptied from the stomach than solids young husband erectile dysfunction buy cialis black 800 mg fast delivery, liquid or blenderized food will be better tolerated which antihypertensive causes erectile dysfunction discount cialis black 800 mg buy online. For patients with severe gastroparesis who do not respond to the measures outlined above erectile dysfunction daily medication cialis black 800 mg buy without a prescription, it may be necessary to bypass the stomach with a jejunal feeding tube. This procedure should be preceded by a trial of nasojejunal feeding for a few days of with infusion rates of at least 60 mL iso-osmolar nutrient per hour. It is preferable to place jejunal feeding tubes directly into the jejunum either by endoscopy, or if necessary by laparoscopy or mini laparotomy, rather than via percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tubes. Such tubes allow restoration of normal nutritional status but they are not without adverse effects. There is no evidence to suggest that gastrectomy relieves symptoms or enhances quality of life. Patients with gastroparesis often have concomitant small intestinal denervation which is likely to cause persistent symptoms after gastrectomy [27,77]. If the patient remains symptomatic, other prokinetic agents may be considered as adjuncts. During acute administration, it initially enhances gastric emptying of liquids in patients with diabetic gastroparesis, but its symptomatic efficacy is probably related to its central antiemetic effects. Its long-term use is restricted by a decline in efficacy and by a troubling incidence of central nervous system side effects. Endoscopic injection of botulinum toxin into the pylorus was not effective in controlled studies primarily of patients with idiopathic gastroparesis [79,80]. While there are no studies in patients with diabetes and constipation, lubiprostone should be considered in patients who have not responded to osmotic agents. References Diabetic diarrhea Diabetic diarrhea is treated symptomatically with loperamide, preferably administered 30 minutes before meals, in the dose range of 216 mg/day. Consumption of artificial sweeteners that contain the osmotically active sugar substitute sorbitol should be reduced. Amitriptyline, which has anticholinergic effects, may reduce intestinal cramping and transit. Octreotide (2550 g subcutaneously 510 minutes before meals) delays small intestinal transit [84] and may also reduce secretory diarrhea associated with rapid intestinal transit [85]. While it has been suggested that octreotide reduces small bowel bacterial overgrowth in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction [86], this study assessed for bacterial overgrowth by breath testing. Indeed, by delaying small intestinal transit, octreotide may predispose to bacterial overgrowth. In addition, pelvic floor retraining with biofeedback therapy can improve rectal sensation, and enhance coordination between perception of rectal distention and contraction of the external anal sphincter [44]; however, biofeedback therapy is less effective in patients with markedly reduced rectal sensation. A descending colostomy may be required and may improve the quality of life in patients with severe diarrhea associated with fecal incontinence. Gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetic patients: lack of association with neuropathy [see Comment]. The Rochester Diabetic Neuropathy Study: reassessment of tests and criteria for diagnosis and staged severity. Gastrointestinal tract symptoms among persons with diabetes mellitus in the community. Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms associated with diabetes mellitus: a population-based survey of 15000 adults. The incidence, prevalence, and outcomes of patients with gastroparesis in Olmsted County, Minnesota, from 1996 to 2006. Impact of chronic gastrointestinal symptoms in diabetes mellitus on health-related quality of life. A longitudinal study of gastric emptying and upper gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with diabetes mellitus [see Comment]. Chronic diarrhea in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and an approach to diagnosis and treatment.
We are dedicated to providing clinically useful erectile dysfunction pills gnc quality 800 mg cialis black, cost-effective testing strategies for patient care erectile dysfunction vitamins purchase cialis black 800 mg mastercard. Development erectile dysfunction natural cialis black 800 mg order online, validation erectile dysfunction pills amazon buy cialis black 800 mg low price, and implementation of new and improved laboratory methods are major components of that commitment. Each assay utilized at Mayo Clinic, whether developed on site or by others, undergoes an extensive validation and performance documentation period before the test becomes available for clinical use. Validations follow a standard protocol that includes: · · · Accuracy Precision Sensitivity Specificity and interferences Reportable range Linearity Specimen stability Specimen type comparisons Urine preservative studies: stability at ambient, refrigerated, and frozen temperatures and with 7 preservatives; at 1, 3, and 7 days Comparative evaluation: with current and potential methods Reference values: using medically evaluated healthy volunteers, male and female, across age groups. The number of observations required for each test is determined by biostatistic analysis. Unless otherwise stated, reference values provided by Mayo Medical Laboratories are derived from studies performed in our laboratories. When reference values are obtained from other sources, the source is indicated in the "Reference Values" field. Time-Sensitive Specimens Please contact Mayo Laboratory Inquiry at 800-533-1710 or 507-266-5700 prior to sending a specimen for testing of a time-sensitive nature. We consider laboratory services as part of the patient care continuum wherein the needs of the patient are paramount. Unlisted Tests Mayo Medical Laboratories does not list all available test offerings in the paper catalog. New procedures are developed throughout the year; therefore, some tests are not listed in this catalog. Although we do not usually accept referred tests of a more routine type, special arrangements may be made to provide your laboratory with temporary support during times of special need such as sustained instrumentation failure. For information about unlisted tests, please call Mayo Laboratory Inquiry at 800-533-1710 or 507-2665700. Unsatisfactory Analytic Results If Mayo Medical Laboratories is unable to obtain a satisfactory analytic result, there is no charge. The disease is preventable by vaccination with tetanus toxoid (formaldehyde-treated tetanospasmin). Tetanus toxoid is an excellent immunogen; it stimulates development of antitetanus toxoid antibodies. An absence of antibody formation postvaccination may relate to immune deficiency disorders, either congenital, acquired, or iatrogenic due to immunosuppressive drugs. Useful For: Assessment of an antibody response to tetanus toxoid vaccine May be used to aid diagnosis of immunodeficiency Interpretation: Results > or =0. Some cases of tetanus, usually mild, occasionally have been observed in patients who have a measurable serum level of 0. The majority of vaccinated individuals should demonstrate protective levels of antibody >0. Bjorkholm B, Wahl M, Granstrom M, Hagberg L: Immune status and booster effects of low doses of tetanus toxoid in Swedish medical personnel. Vitamin D in the body is derived from 2 sources: exogenous (dietary: D2 and D3) and endogenous (biosynthesis: D3). Endogenous D3 is produced in the skin from 7-dehydrocholesterol, under the influence of ultraviolet light. It stimulates calcium absorption in the intestine and its production is tightly regulated through concentrations of serum calcium, phosphorus, and parathyroid hormone. Some patients with granulomatous diseases (eg, sarcoidosis) and malignancies containing nonregulated 1-alpha hydroxylase in the lesion may have elevated 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D levels and hypercalcemia. However, in the presence of renal disease, 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D levels may be needed to adequately assess vitamin D status. Reference Values: Males <16 years: 24-86 pg/mL > or =16 years: 18-64 pg/mL Females <16 years: 24-86 pg/mL > or =16 years: 18-78 pg/mL Clinical References: 1. Elevated levels of tryptase, N-methylhistamine or 11 beta-prostaglandin F2 alpha are consistent with the diagnosis of systemic mast cell disease. However, aspirin use is not without risk, and is associated with higher frequencies of gastrointestinal bleeding and hemorrhagic stroke. Reference Values: Males > or =18 years: 0-1,089 pg/mg of creatinine Females > or =18 years: 0-1,811 pg/mg of creatinine Reference values have not been established for patients that are <18 years of age. Reference intervals apply to patients not taking agents known to influence platelet function (aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, thienopyridines, etc.
Syndromes
- Decreased alertness, drowsiness, confusion
- Down syndrome
- Weakness
- The puncture site is covered to stop any bleeding.
- Blood clots in the legs that may travel to the lungs
- Avoid exposure to substances that give you allergic reactions.
- Vitamin B12 level (serum)
- Ask about your recent mood swings and for how long you have had them.
- An aneurysm of the heart wall
Investigation of this intriguing possibility is in its infancy and further research is needed erectile dysfunction va benefits cheap cialis black 800 mg buy on line. It is thought that such cytokines may be released in increased amounts from adipose tissue in conditions including diabetes and obesity as people age erectile dysfunction causes tiredness generic 800 mg cialis black with mastercard, and this may interfere with insulin action erectile dysfunction recreational drugs 800 mg cialis black buy fast delivery. Loss of normal diurnal variation in cortisol levels together with non-suppression of cortisol release in response to exogenous steroid administration have long been noted as hallmarks of depressive illness viagra causes erectile dysfunction buy 800 mg cialis black free shipping, particularly the "melancholic" subtype. It is suggested that this may lead to increased glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis, lipolysis and inhibition of peripheral glucose transport and utilization [15]. Non-diabetic patients with depression have been shown to have increased insulin resistance, but further investigation of this mechanism is warranted. Glucose transport in the brains of people with depression has also been shown to be abnormal [15]. Proposed mechanisms linking depression and diabetes Psychosocial factors Most studies confirm that risk factors for depression in otherwise healthy individuals operate equally in people with diabetes. Thus, socioeconomic hardship, poor education, stressful life events and lack of social support are all important [8]. There is relatively little evidence that people with diabetes differ greatly with respect to these types of risk factors, and it can be concluded that much depression in people with diabetes may be "independent" of the presence of the disease, an issue that may be particularly important when it comes to management planning. Early nutrition One putative common risk factor that may increase the risks of both of diabetes and depression is that of disrupted nutrition during fetal life. There are now over 38 reports linking poor fetal growth with impaired glucose metabolism in later life [9]. Similarly, the risk of depression has been found to be associated with low birth weight for both young and older adults [10]. Furthermore, data from the Dutch Hunger Winter study showed that exposure to famine during the second Depression and glycemic control Several studies have demonstrated an association between the severity of depressive symptoms and the level of glycemic control as assessed by glycosylated hemoglobin level (HbA1c) [16], although the size of this effect has been generally modest, and may be explained by confounders such as the presence of microvascular complications. Most studies have been cross-sectional in 942 Psychiatric Disorders and Diabetes Chapter 55 nature, although some treatment studies have suggested that improvements in glycemic control are associated with reduction of depressive symptoms. Knowledge of appropriate counseling techniques and appropriate drug therapy is important, as well as an awareness of the need for prompt referral to specialists of those in whom psychologic difficulties continue to interfere significantly with well-being or diabetes self-management. It may be better to use a very brief clinical interview using three questions [25]. Initially, the patient is asked: · During the past month, have you been bothered by having little interest or pleasure in doing things? If the answer to either of these is "yes," the patient should then be asked if they want help with this problem. Depression and complications There seems to be little doubt that the risk of depression increases as microvascular and macrovascular complications accrue over the course of the disease [17]. The evidence is less strong that the presence of depression increases the risk of developing complications, although the fact that self-care and resulting glycemic control are impaired would lead to this expectation. One complication that may have a particular association with depression is that of peripheral neuropathic pain. Recent studies suggest that not only is chronic pain a risk factor for depression, but the presence of depression may itself worsen the experience of pain. Management of people with diabetes and depression At present, advice for the management of patients with comorbid depression and diabetes is based on evidence derived from populations without diabetes because the number of treatment studies in people with diabetes is as yet too small to lead to robust conclusions. The main aims of treatment are to reduce depressive symptoms and to improve self-care, glycemic control and diabetes outcomes. A major difficulty for most clinics is the lack of readily available specialist mental health input, and this has been a disincentive for services to engage actively in tackling this important clinical problem. By contrast, guidelines are now including the issue of psychologic well-being, increasing the need for attention to be paid to it. It should be possible for most clinics to provide "first response" management for simple depressive disorders, although specialist help will still be required for more complex cases, where there is diagnostic uncertainty or lack of response to initial treatment. Assessment and management of suicide risk is a particularly important issue, although fortunately rare in most clinic settings. Case history 1: A woman with diabetes and depression Joan is a 62-year-old married woman who has had type 2 diabetes for 15 years, which is treated by diet and oral hypoglycemic medication.
Discount cialis black 800 mg buy online. Diabetes and ED.
References
- The United Kingdom EVAR Trial Investigators. Endovascular versus open repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1863-1871.
- Doctor N, Hussain Z: Bilateral pneumothorax associated with laparoscopy, Anesthesia 28:75-81, 1973.
- Jorgensen, J.O., Hanel, K., Lalak, N.J. et al. Thromboembolic complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. BMJ 1993;306:518-519.
- Zanaria E, Bardoni B, Dabovic B, et al: Xp duplications and sex reversal, Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 350(1333):291n296, 1995.
- Santillan R, Maestre JM, Hurle MA, et al: Enhancement of opiate analgesia by nimodipine in cancer patients chronically treated with morphine: A preliminary report, Pain 58(1):129-132, 1994.
- Dimopoulos M, Siegel DS, Lonial S, et al. Vorinostat or placebo in combination with bortezomib in patients with multiple myeloma (VANTAGE 088): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind study. Lancet Oncol 2013;14(11):1129-1140.
- Chen E, Miller GE, Walker HA, et al. Genome-wide transcriptional profiling linked to social class in asthma. Thorax 2009; 64: 38-43.
- Swan A, Heywood B, Chapman B, Seward H, Dieppe P. Evidence for a causal relationship between the structure, size, and load of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals, and attacks of pseudogout. Ann Rheum Dis 1995; 54(10):825-30.