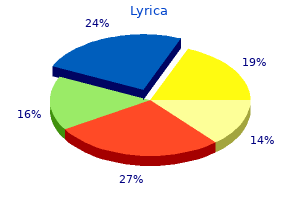
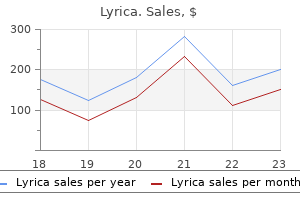
Lyrica
Christopher J Earley, M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
- Professor of Neurology

https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0006845/christopher-earley
Efficacy mental disorders axis 3 , safety mental treatment 100 , and tolerability of augmentation pharmacotherapy with aripiprazole for treatmentresistant depression in late life: a randomized mental disorders misconceptions , double-blind mental movement therapy , placebo-controlled trial. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 15 antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia: a multiple-treatments metaanalysis. A meta-analysis of head-to-head comparisons of second-generation antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia. Lurasidone as adjunctive therapy with lithium or valproate for the treatment of bipolar I depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Lurasidone monotherapy in the treatment of bipolar I depression: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled study. Risperidone in preschool children with autistic spectrum disorders: an investigation of safety and efficacy. The efficacy and safety of aripiprazole as adjunctive therapy in major depressive disorder: a second multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. A placebo-controlled, fixed-dose study of aripiprazole in children and adolescents with irritability associated with autistic disorder. Safety and tolerability of aripiprazole for irritability in pediatric patients with autistic disorder: a 52-week, openlabel, multicenter study. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with schizophrenia. Risperidone for the core symptom domains of autism: results from the study by the Autism Network of the Research Units on Pediatric Psychopharmacology. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of maintenance treatment with adjunctive risperidone long-acting therapy in patients with bipolar I disorder who relapse frequently. A three-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of asenapine in the treatment of acute mania in bipolar mania and mixed states. Asenapine for long-term treatment of bipolar disorder: a double-blind 40-week extension study. Asenapine in the treatment of acute mania in bipolar I disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial. Lurasidone in the treatment of schizophrenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-and olanzapinecontrolled study. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of aripiprazole lauroxil in acute exacerbation of schizophrenia. Treatments for schizophrenia: a critical review of pharmacology and mechanisms of action of antipsychotic drugs. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years-Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, 11 sites, United States, 2012. Efficacy of second generation antipsychotics in treating acute mixed episodes in bipolar disorder: a metaanalysis of placebo-controlled trials. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with tic disorders. Risperidone in children with autism: randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Lurasidone in the treatment of acute schizophrenia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Orange Book: Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations [database on the internet]. Aripiprazole in the treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autistic disorder. Aripiprazole augmentation of selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder. Olanzapine vs risperidone in the treatment of manic or mixed states in bipolar I disor der: a randomized, double-blind trial.
Intermittent exposure to near-saturation vapor concentrations of heated Aroclor 1242 (8 list of mental disorders caused by bullying . Similar exposures to lower concentrations of heated Aroclors 1242 and 1254 were also found not to produce lethality in these species mental disorders need for attention . Causes of death from acute exposure are unclear mental treatment 2 , but principal signs of toxicity in rats included diarrhea and respiratory depression mental illness jail , and dehydration may be a principal contributing factor (Bruckner et al. Single-dose oral lethality data for species other than rats and minks were not located. At the highest Aroclor 1254 dose of 520 mg/kg/day, 5 of 5 mice died within 7 days, but none of the 5 mice treated with 2. Intermediate-duration gavage and feed studies in rats and mice reported that much higher doses of Aroclor 1254 or 1260 caused death (Garthoff et al. Although this may be due to species differences in susceptibility, the shorter and intermittent duration of exposure (2. There was no attempt to identify or quantitate impurities in the Aroclor 1254 test compound. A single topical dose of 2,273 mg/kg Aroclor 1254 was fatal to hairless mice within 24 hours (Puhvel et al. It was not specified whether all three treated mice died or whether the Aroclor was administered in pure acetone or in acetone-mineral oil emulsion. Cause of death was not reported, and there was no clear trend of toxicity with degree of chlorination. Upper respiratory tract or eye irritation (48%), cough (14%), and tightness of the chest (10%) were noted among 326 capacitor workers exposed to 0. The significance of these effects is unknown due to lack of a control group; however, the prevalence of upper respiratory tract or eye irritation (48%) raises concern that they are exposure-related. Other limitations of this study include discrepancies between the reports of Fischbein et al. Additionally, capacitor manufacturing plants typically used large amounts of volatile degreasing agents that may have contributed to pulmonary symptom complaints. The chest pain symptom was not investigated further and was not attributed to a specific cause. Similar results were initially found in another spirometry study of 179 workers from the same plant population as that studied by Warshaw et al. The occurrence of self-reported respiratory effects was not elevated among residents who lived within 0. Potential respiratory effects have also been reported in Yusho and Yu-Cheng patients. More frequent or severe respiratory infections (Kuratsune 1989; Rogan 1989) and chronic bronchitis accompanied by persistent cough and sputum production (Nakanishi et al. There were no histological alterations in the lungs of rats administered a single 4,000 mg/kg dose of Aroclor 1242 by gavage and evaluated 24 hours posttreatment or in rats treated with 100 mg/kg/day Aroclor 1242 by gavage every other day for 3 weeks (Bruckner et al. No histopathologic changes were observed in the trachea or lungs of male or female rats that were fed Aroclor 1016, 1242, 1254, or 1260 for 24 months at intake levels of 8. Intermediate-duration dietary exposure to single congeners did not result in histological damage in the lungs of rats fed diets providing #4. Mortality from circulatory diseases was significantly increased in the high exposure subgroup of a cohort of 242 male capacitor manufacturing workers with >5 years exposure and >20 years latency (Gustavsson and Hogstedt 1997). The inconsistent results of these studies could be due to differences in exposure levels, durations, and latencies, as well as types of Aroclors and cohort sizes. Blood pressure measurements (systolic and diastolic) and electrocardiograms were normal in 194 capacitor plant workers (152 male, 43 female) who were exposed to Aroclors 1254, 1242, and 1016 for an average duration of 17 years (Lawton et al. A 30% increase over the national average incidence of borderline and definite hypertension was observed in Triana, Alabama, residents (Kreiss et al. Pericardial edema occurred in four of six monkeys given 12 mg/kg/day Aroclor 1248 in the diet for 3 months (Allen et al.
Levels and patterns of polychlorinated biphenyls in water collected from the San Francisco Bay and estuary mental disorders glossary , 1993-95 mental conditions in cats . In: Proceedings of the National Conference on Polychlorinated Biphenyls mental health unit , Chicago mental treatment urticaria , 1975. Number and identity of anthropogenic substances known to be present in Baltic seals and their possible effects on reproduction. Congener-specific determination of polychlorinated biphenyls and organochlorine pesticides in human milk from Norwegian mothers living in Oslo. Permeability and vascularity of the developing brain: cerebellum vs cerebral cortex. Public health implications of persistent toxic substances in the Great Lakes and St. Promotion of endometriosis in mice by polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins, dibenzofurans, and biphenyls. Long-term trends and sources of organochlorine contamination in Canadian Tundra peregrine falcons, falco peregrinus tundrius. Alteration of the immune response of channel catfish (ictalurus punctatus) by polychlorinated biphenyls. In: Symposium on pathobiology of environmental pollutants: Animal models and wildlife as monitors. Determination of polychlorinated biphenyls in human foodstuffs and tissues: Suggestions for a selective congener analytical approach. Vitamins A1, A2, and E in minks exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclor 1242) and copper, via diet based on freshwater or marine fish. Cytogenetic analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes in workers occupationally exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls. Highly hydrogenated dietary soybean oil modifies the responses to polychlorinated biphenyls in rats. Metabolism of dichlorobiphenyls by highly purified isozymes of rat liver cytochrome P-450. Accumulated pesticide and industrial chemical findings from a ten-year study of ready-to-eat foods. Isomer-specific analysis and toxic evaluation of polychlorinated biphenyls in striped dolphins affected by an epizootic in the western Mediterranean Sea. Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in foodstuffs from Asian and oceanic countries. Polychlorinated naphthalenes and polychlorinated biphenyls in fishes from Michigan waters including the Great Lakes. Semi-empirical estimation of sorption of hydrophobic pollutants on natural sediments and soils. Comparative toxicity of polychlorinated biphenyl and polybrominated biphenyl in the rat thyroid gland: Light and electron microscopic alterations after subacute dietary exposure. Effect of dietary level of ascorbic acid on the growth, hepatic lipid peroxidation, and serum lipids in guinea pigs fed polychlorinated biphenyls. Effects of dietary polychlorinated biphenyls and protein level on liver and serum lipid metabolism of rats. Induction of hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes by methylsulphonyl metabolites of polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in rats. Polychlorobiphenyls and persistent organochlorine pesticides in sea water at the pg l1 level. Polychlorinated biphenyl contamination in selected estuarine and coastal marine finfish and shellfish of New Jersey. Reproductive toxicity of Aroclor-1254: Effects on oocyte, spermatozoa, in vitro fertilization, and embryo development in the mouse. Comparative analyses of contaminant levels in bottom feeding and predatory fish using the National Contaminant Biomonitoring Program data. Induction of adenofibrosis and hepatomas in the liver of Balb/cJ mice by polychlorinated biphenyls (Aroclor 1254). Mortality in male and female capacitor workers exposed to polychlorinated biphenyls. Morphological changes in livers of rats fed polychlorinated biphenyls: Light microscopy and ultrastructure.
Importance and management the limited evidence suggests that ashwagandha might have bloodglucose-lowering effects mental illness case studies . Until further information is available mental illness journal , if a patient taking antidiabetic drugs wants to take ashwagandha it may be prudent to discuss these potential additive effects mental therapy 1000 , and advise an increase in blood-glucose monitoring should an interaction be suspected mental therapy kicks . However, bear in mind that, although ashwagandha has been used for a wide number of complaints, it does not appear to be used for diabetes, suggesting that any effects are mild, and probably not clinically relevant. Hypoglycemic, diuretic and hypocholesterolemic effect of winter cherry (Withania somnifera, Dunal) root. Ashwagandha + Digoxin Ashwagandha has been shown to interfere with some methods of measuring serum digoxin levels; see Ashwagandha + Laboratory tests below. Ashwagandha + Thyroid and Antithyroid drugs Limited evidence suggests that ashwagandha increases thyroid hormone levels and therefore interferes with the control of hypoand hyperthyroidism. Clinical evidence A 32-year-old healthy woman developed clinical symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, and was found to have elevated levels of thyroid hormones when she increased the dose of capsules containing ashwagandha herbal extract that she had been taking for chronic fatigue. Ashwagandha does not interfere with in vitro assays for carbamazepine, gentamicin, paracetamol, phenytoin, Ashwagandha Experimental evidence In a study in mice, ashwagandha root extract 1. Importance and management Although the evidence is limited, until more is known, it might be 43 prudent to advise caution if patients taking levothyroxine (or other thyroid hormones) want to take ashwagandha because of the possibility of an increase in effects. Furthermore, on the basis of this evidence, ashwagandha may be expected to antagonise the effects of antithyroid drugs, such as propylthiouracil. In both cases it may be prudent to consider monitoring thyroid function tests if symptoms of hypo- or hyperthyroidism begin to emerge. Changes in thyroid hormone concentrations after administration of ashwagandha root extract to adult male mice. For information on the pharmacokinetics of individual flavonoids present in asparagus, see flavonoids, page 186. Constituents Asparagus contains saponins called asparagosides, steroidal glycosides, asparagusic acid and its derivatives, flavonoids (including rutin, kaempferol and quercetin) and various amino acids and polysaccharides. Interactions overview No interactions with asparagus found; however, note that asparagus contains a moderate amount of vitamin K and may therefore reduce the effectiveness of warfarin and other similar anticoagulants if eaten in large quantities. For information on the interactions of individual flavonoids present in asparagus, see under flavonoids, page 186. Use and indications the root and green parts of asparagus have been used as a diuretic, laxative, cardiac tonic and sedative. The young 44 Asparagus 45 Asparagus + Food No interactions found, but note that asparagus is extensively used as a foodstuff. Asparagus + Warfarin and related drugs Patients taking coumarins and indanediones should avoid taking excessive amounts of asparagus because of its vitamin K1 content. Evidence, mechanism, importance and management Asparagus1 contains a moderate amount of vitamin K1, which reduces the effect of coumarin and indanedione anticoagulants, which are vitamin K antagonists. Patients taking these anticoagulants are advised to maintain a regular amount of vitamin K from the diet. A Astragalus Astragalus membranaceus Bunge (Fabaceae) Synonym(s) and related species Huang qi. Not to be confused with the pharmaceutical excipient, tragacanth (Astragalus gummifer). Pharmacokinetics Few data are available, but in a study in one healthy subject, who was given astragalus root decoction orally twice daily before meals of bread and honey for 5 days, urine samples were found to contain calycosin and formononetin and various isoflavonoid glucuronide metabolites. These data, and data from in vitro studies, demonstrate that the isoflavones in astragalus could be absorbed and metabolised by the intestine. Isoflavones are also present, mainly glycosides of calycosin and formononetin, with astrapterocarpan, kumatakenin and numerous hydroxyl and methoxyl derivatives of pterocarpan and isoflavan, and a series of polysaccharides known as astragaloglucans. Interactions overview Astragalus appears to alter the immune response, but the effect this has on treatment with interleukins, interferons, antiretrovirals and antineoplastics does not appear to be established. For information about the interactions of individual isoflavones present in astragalus, see under isoflavones, page 258. Absorption and metabolism of Astragali radix decoction: in silico, in vitro, and a case study in vivo. Use and indications Astragalus is traditionally used in Chinese medicine as a tonic to strengthen the immune system, for viral infections, fatigue and loss of blood. It is now used as a liver protectant, an adjunct in chemotherapy and impaired immunity, and for 46 Astragalus 47 Astragalus + Antineoplastics Astragalus improved the response to chemotherapy with mitomycin, a vinca alkaloid and cisplatin in one study.
. Professor Green on mental illness.
References
- Xie Q, Hao Y, Tao L, et al. Lysine methylation of FOXO3 regulates oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell death. EMBO Rep 2012;13(4):371-7.
- Manning J, Korda A, Benness C, et al: The association of obstructive defecation, lower urinary tract dysfunction and the benign joint hypermobility syndrome: a case-control study, Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct 14:128n132, 2003.
- Dharmawardana PG, Giubellino A, Bottaro DP: Hereditary papillary renal carcinoma type I, Curr Mol Med 4:855n868, 2004.
- Van de Werf F. The history of coronary reperfusion. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2510-2515.
- Fitzgerald RC, Caldas C. Familial gastric cancer - clinical management. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2006;20:735.