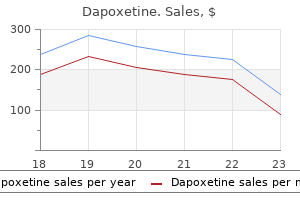
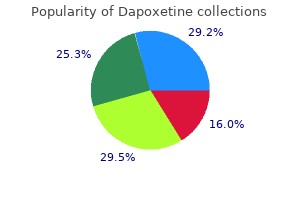
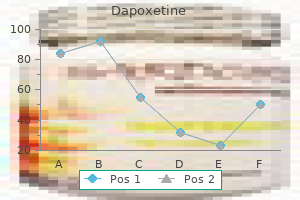
Dapoxetine
Manju Monga, MD
- Professor
- Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Reproductive Sciences
- University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
- Houston, Texas
All samples should be kept on ice or at 4 C during sample preparation or handling does erectile dysfunction cause low sperm count dapoxetine 90 mg low cost. Samples should be stored at А80 C erectile dysfunction juice discount dapoxetine 90 mg with visa, but erectile dysfunction doctors in kansas city cheap 30 mg dapoxetine free shipping, ideally erectile dysfunction doctors in colorado springs dapoxetine 30 mg purchase without a prescription, samples should be immediately analyzed. In addition to keeping samples cold, there are four other issues that are critical to the successful preparation of metabolomics samples: (1) speed, (2) consistency, (3) random processing of samples, and (4) the efficient removal of all biomolecules and cell debris [6]. Metabolites can chemically degrade or transform within milliseconds due to enzymatic activity, oxidation, chemical instability, or any number of other chemical processes [44]. Accordingly, rapidly inactivating and removing all biomolecules and cell debris (usually through methanol/ethanol precipitation) that may transform or bind a metabolite is a necessary step of the protocol (see Note 9). In addition to the cell extract, the media should also be analyzed for metabolomics changes as many metabolites get exchanged or effluxed outside of the cell. Using a cell scraper, detach and collect cell debris and methanol in a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube. Confirm cell detachment using a microscope and repeat lyse and quenching if necessary. Centrifuge the 2 mL microcentrifuge tube for 5 min at 15,000 В g and 4 C to pellet the cell debris. Centrifuge the cell pellet with the extraction solvent for 5 min at 15,000 В g at 4 C to pellet the cell debris. Collect the supernatant, and transfer it to the 2 mL microcentrifuge tube containing the original methanol extract. Collect the supernatant, and transfer it to the 2 mL microcentrifuge tube containing the two previous extraction supernatants. We have used the subchronic exposure to pesticides and metals [15], but the protocol described can be applied to all murine animal models. We have successfully used 200 mg/kg of 13C6-glucose at a total volume of 100 L administered to fasted mice (overnight) via intra-orbital injection to label metabolites extracted from mouse brain tissue. Harvest and dissect the mice brain tissue (1520 min after the injection of 13C-labeled tracer if used, see. Transfer the tissue to a 2 mL microcentrifuge tube containing Lysing Matrix D, and weigh the amount of tissue harvested from the mice, and immediately freeze the tissue with liquid nitrogen. Homogenize the sample in a FastPrep with Lysing Matrix D at 1300 rpm for 20 s and for two cycles. Normalize the metabolomics sample to the tissue weight by diluting all of the samples to a final volume of 1. Add as much of a 1:1 mixture of methanol and water prechilled to А20 C as needed to achieve a final volume of 1. Each sample is added to a 96-well plate SampleJet configuration equilibrated to 4 C to prevent metabolite degradation (see. Dissolve lyophilized cell-free lysates or tissue extracts in 20 L of reconstitution solution and vortex for 30 s. Centrifuge the solution at 14,000 В g for 10 min to remove any particulate matter. Place all vials into the autosampler equilibrated to 4 C to prevent metabolite degradation (see. Log into an account on the spectrometer workstation and start the Topspin software. The spectrometer is locked onto the D2O solvent frequency using the Bruker command, lock D2O. This will initiate an automated gradient shimming procedure, which may take a few minutes to complete (see Note 11). The 90-degree pulse length (s) is determined by measuring a null spectrum with an approximate 360-degree pulse using the Bruker zg pulse sequence (see Note 12). The spectrum is collected with 2 K data points and a spectrum width of 4734 Hz in the direct dimension and 64 data points and a spectrum width of 18,864 Hz in the indirect dimension (see Note 14).
In women impotence from prostate surgery buy dapoxetine 30 mg cheap, vulvovaginitis is the most common manifestation and presents with pruritus vulvae that can be intense and distressing erectile dysfunction treatment ottawa discount dapoxetine 60 mg with amex. The vulva appears erythematous and fissured erectile dysfunction treatment in mumbai 60 mg dapoxetine purchase with mastercard, with peripheral pustulation in severe cases impotence after robotic prostatectomy buy 90 mg dapoxetine mastercard. It may be particularly troublesome while a patient is hyperglycemic and glycosuric [68]. Candidal balanitis, balanoposthitis and phimosis occur less commonly in men, but could be a presenting feature [69]. Candidal angular stomatitis and an atrophic tongue resembling median rhomboid glossitis are oral manifestations of diabetes. Oral candidiasis occurs more commonly in patients with diabetes who smoke or wear dentures [70]. Candidal intertrigo occurs on opposing surfaces under the breast, in the groins and axillae, or in the folds of the abdominal skin. Scratching of the areas involved with Candida infection can result in bacterial superinfection. Candida infection of the hands and feet are probably equally seen in those with diabetes and the non-diabetic population, but tends to be more severe in the former. Chronic paronychia presents as swelling and erythema around the lateral nailfold, with more severe involvement leading to onycholysis (Figure 47. Microscopic examination and culture of the extruded material will confirm the presence of Candida. Less common than paronychia is infection of the web space between the middle and fourth finger (erosion interdigitale blastomycetica) [71]. Exclusion of moisture is an essential aspect to the treatment, and systemic antifungal drugs. Inappropriate treatment with steroids or antibiotics can worsen Candida infection at any site. Bacterial infections Furuncles, carbuncles, styes and erythrasma were particularly frequent before the introduction of insulin and antibiotics, and skin infections from Staphylococcus aureus are still probably more common in the patient with diabetes than in the non-diabetic population. Increased rates of colonization with staphylococci has been reported in those with poorly controlled diabetes [72]. Severe ("malignant") otitis externa is an uncommon but potentially lethal infection caused by invasive Pseudomonas spp. The condition occurs in elderly patients with diabetes and manifests as purulent discharge with severe pain in the external ear. It progresses from cellulitis to osteomyelitis, meningitis and cerebritis with a high mortality [73]. Erythrasma, caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum, is rare but occurs with increased frequency in obese patients with diabetes. It presents as a red shiny or scaly patch in the intertriginous areas and with ultraviolet light exhibits a characteristic coral-red fluorescence. Unusual infections with coliforms or anaerobes occur in those with diabetes as can Pseudomonas infections of the toe web spaces or nailfold (paronychia) and secondary infection of venous ulcers [74]. Anaerobic cellulitis with Clostridium species can occur in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis, requiring treatment with metabolic control, aggressive dйbridement of devitalized tissue and intravenous antimicrobial therapy [64]. Necrotizing fasciitis is a potentially lethal skin and soft tissue infection that is more common in those with diabetes [68]. Streptococcus pyogenes, anaerobic streptococci, Bacteroides and Staphylococcus aureus are some of the organisms associated with necrotizing fasciitis. This infection can extend from trivial wounds such as furuncles, insect bites and injection sites, or sometimes begin from decubitis ulcers. Rapid progression ensues, with extensive tissue destruction and severe systemic toxicity, leading to death [75]. This condition should be considered in patients with diabetes and cellulitis who have associated systemic features such as tachycar- 781 Part 9 Other Complications of Diabetes dia, leukocytosis, marked hyperglycemia or acidosis.
The unique cytoarchitecture of human pancreatic islets has implications for islet cell function erectile dysfunction scrotum pump dapoxetine 30 mg on line. Real-time erectile dysfunction typical age 30 mg dapoxetine mastercard, multidimensional in vivo imaging used to investigate blood flow in mouse pancreatic islets erectile dysfunction from diabetes dapoxetine 90 mg purchase on line. Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion: implications for health and disease erectile dysfunction on coke discount 90 mg dapoxetine mastercard. The possible importance of contact between pancreatic islet cells for the control of insulin release. Spontaneous reassociation of dispersed adult rat pancreatic islet cells into aggregates with three-dimensional architecture typical of native islets. An islet is greater than the sum of its parts: the importance of intercellular communication in insulin secretion. Loss of connexin 36 channels alters beta-cell coupling, islet synchronization of glucose-induced Ca2+ and insulin oscillations, and basal insulin release. Conclusions Pancreatic islets of Langerhans are complex endocrine organs containing several different types of endocrine cells, with extensive vasculature and autonomic nerve supply. Interactions between the islet cells, the autonomic nervous system and hormones secreted by the gastrointestinal system and adipose tissue enable the appropriate release of islet hormones to regulate metabolic fuel usage and storage. Cx36 makes channels coupling human pancreatic beta-cells, and correlates with insulin expression. E-cadherin interactions regulate beta-cell proliferation in islet-like structures. Dual effect of cellcell contact disruption on cytosolic calcium and insulin secretion. EphA-Ephrin-A-mediated beta cell communication regulates insulin secretion from pancreatic islets. Somatostatin secreted by islet delta-cells fulfills multiple roles as a paracrine regulator of islet function. Glucose or insulin, but not zinc ions, inhibit glucagon secretion from mouse pancreatic alpha-cells. A role for the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor in cellcell communication in pancreatic islets of Langerhans. Dopamine D2-like receptors are expressed in pancreatic beta cells and mediate inhibition of insulin secretion. Heme oxygenase and carbon monoxide: regulatory roles in islet hormone release a biochemical, immunohistochemical, and confocal microscopic study. Proteins associated with immunopurified granules from a model pancreatic islet beta-cell system: proteomic snapshot of an endocrine secretory granule. Zincligand interactions modulate assembly and stability of the insulin hexamer: a review. Microtubules and beta cell function: effect of colchicine on microtubules and insulin secretion in vitro by mouse beta cells. Suppression of the expression of a pancreatic beta-cell form of the kinesin heavy chain by antisense oligonucleotides inhibits insulin secretion from primary cultures of mouse beta-cells. Molecular mechanisms involved in secretory vesicle recruitment to the plasma membrane in beta-cells. Kinectin participates in microtubule-dependent hormone secretion in pancreatic islet beta-cells. Expression and localisation of synaptotagmin isoforms in endocrine beta-cells: their function in insulin exocytosis. Human and rat beta cells differ in glucose transporter but not in glucokinase gene expression. Mutations in the sulfonylurea receptor gene in familial persistent hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia of infancy. Fast exocytosis with few Ca2+ channels in insulin-secreting mouse pancreatic B cells. Protein kinases, protein phosphorylation, and the regulation of insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells.
Serum glucose level and diabetes predict tissue plasminogen activator-related intracerebral hemorrhage in acute ischemic stroke erectile dysfunction doctor los angeles order 60 mg dapoxetine mastercard. Predictors of hyperacute clinical worsening in ischemic stroke patients receiving thrombolytic therapy erectile dysfunction treatment options uk generic dapoxetine 90 mg without a prescription. Lack of improvement in patients with acute stroke after treatment with thrombolytic therapy erectile dysfunction pills photos generic dapoxetine 30 mg buy on-line. Intense metabolic control by means of insulin in patients with diabetes mellitus and acute myocardial infarction erectile dysfunction treatment ppt 90 mg dapoxetine purchase fast delivery. A randomized, controlled pilot study to investigate the potential benefit of intervention with insulin in hyperglycaemic acute ischaemic stroke patients. Stroke unit care and outcome: results from the 2001 National Sentinel Audit of Stroke (England, Wales, and Northern Ireland). Primary prevention of cardiac disease and type 2 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 708 Cerebrovascular Disease Chapter 42 diabetes in patients at metabolic risk: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. Amplified benefit of clopidogrel versus aspirin in patients with diabetes mellitus. Antiplatelet cilostazol is beneficial in diabetic and/or hypertensive ischemic stroke patients. Choosing antithrombotic therapy for elderly patients with atrial fibrillation who are at risk for falls. Sillesen Department of Vascular Surgery, Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark · Peripheral arterial disease is very common, affecting up to 30% of all people with diabetes. Introduction Peripheral vascular disease includes diseases to arteries and veins outside the thoracic region. Special considerations in patients with diabetes are dealt with in relevant sections; for example, infection in an ischemic foot in a patient with diabetes is described in the section on critical limb ischemia. Atherosclerosis is the main cause of peripheral arterial vascular disease, and the overall pathogenesis is covered in Chapter 39. It is important to appreciate that the pathogenetic mechanisms of clinical atherosclerosis are dual: chronic obstructive and thrombotic. Whereas the chronic obstructive mechanism is the main cause of lower limb ischemia, also in patients with diabetes, it is often preceeded by a thrombotic event; a patient with mild claudication suddenly experiences significantly shortening of walking distance or sudden onset of rest pain. Of course, a heart attack or stroke in a patient with claudication is also a thrombotic event in a patient with chronic obstructive disease. In general, patients with diabetes more often develop symptoms of atherosclerotic complications, they do it at a younger age Textbook of Diabetes, 4th edition. Peripheral arterial disease Peripheral arterial disease is a chronic condition that, like atherosclerosis in other vascular beds, develops over decades. On average, symptoms from the lower limbs develop 510 years later than from the coronary circulation. Acute ischemia may develop because of: 1 Thrombosis in a vessel with pre-existing atherosclerotic plaques and/or stenosis; 2 Embolism. Claudication is twice as common in those with diabetes than those who do not have diabetes. The abnormal metabolic state that accompanies diabetes directly contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. Pro-atherogenic changes include increases in vascular inflammation and alterations in multiple cell types. Obviously, the long-term accumulation of lipids in the vessel wall is important and sudden local thrombosis can occur at any time, although in most cases this happens after symptoms (claudication) have developed. To reach the stage of critical limb-threatening ischemia, advanced atherosclerosis has developed. Often, multiple segments of the arterial tree from the aorta to the foot are affected (stenotic and/or occluded). In people with diabetes, the atherosclerotic lesions are more peripherally located than in people without diabetes. Whereas the iliac and femoral arteries are most commonly stenotic and/or occluded in individuals without diabetes, in those with diabetes, it is most often the crural arteries that are severely affected by atherosclerosis. This poses a challenge for revascularization because the results in general are better the more proximal the reconstruction. The most reliable method for assessment of peripheral perfusion in those with diabetes is measurement of toe pressure. A toe pressure below 2025 mmHg signals a poor chance of healing of a peripherally located ulcer.
Buy discount dapoxetine 30 mg line. Marsh Benjamin MD – Essentia Health.
References
- Lezrek M, Bazine K, Ammani A, et al: Needle renal displacement technique for the percutaneous approach to the superior calix, J Endourol 25:1723-1726, 2011.
- Kurian AW, Sigal BM, Plevritis SK. Survival analysis of cancer risk reduction strategies for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers. J Clin Oncol 2010;28(2):222-231.
- Moyer VA, US Preventive Services Task Force: Screening for prostate cancer: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement, Ann Intern Med 157:120n134, 2012.
- Douard R, Wind P, Panis Y, et al: Intraoperative endoscopy for diagnosis and management of unexplained gastrointestinal bleeding. Am J Surg 180:181, 2000.
- Pisters PW, Harrison LB, Woodruff JM, et al. A prospective randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in the management of low-grade soft tissue sarcomas of the extremity and superficial trunk. J Clin Oncol 1994;12(6):1150-1155.
- Shimabukuro D, Sakumoto K, Masamot H, et al. A case of congenital high airway obstruction syndrome managed by ex utero intrapartum treatment: case report and review of the literature. Am J Perinatol 2007;24:197-201.
- Hansson GK: Immune mechanisms in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001;21:1876-1890.