Dutasteride
Feroze Mahmood, MD
- Director of Vascular Anesthesia and Perioperative Echocardiography
- Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
- Boston, Massachusetts
Such trait-based approaches presented in this section share the same basic view of educational measurement hair loss edges order dutasteride 0.5 mg line. Something of this is reflected in criticisms of current approaches hair loss zoladex buy 0.5 mg dutasteride visa, and possible future developments hair loss name generic dutasteride 0.5 mg free shipping, which we will consider later hair loss surgery generic dutasteride 0.5 mg amex. The technical apparatus of trait-based measurement, as presented in the chapters in this section, still has much to offer language testing. If such constructions are found practically useful it is partly due to their metaphorical power as accessible, communicative representations of a complex reality. The concept of reliability Reliability equals consistency Reliability in assessment means something rather different to its everyday use. This is indeed one aspect of trustworthiness, as when we speak of a reliable friend, car or train service. Ennis (1999) argues that simple misunderstanding of the term on the part of test users has led to a damaging focus on reliability at the expense of other test qualities. But the result need not be a correct or accurate measure o f what the test claims to measure. Just as a train service can run consistently late, a test may provide an incorrect result in a consistent manner. Nonetheless, a valid test must have acceptable reliability, because without it the results can never be meaningful. Thus a degree o f reliability is a necessary but not sufficient condition o f validity. Reliability and error Quantification o f the consistency and inconsistency in examinee performance constitutes the essence o f reliability analysis. Reliability is defined as the proportion o f variation in scores caused by the ability measured, and not by other factors. This proportion is typically described as a correlation (or correlation-like) coefficient. Depending on the type o f reliability being analysed, what is correlated with what will change; however, all reliability coefficients are interpretable in the sense o f repeated measurement that I describe above. But the fact is, of course, that even the best tests contain error, in its psychometric sense. The tasks in the test version may perform differently to those in another version, and so on. However, the third and fourth sources of error could also be seen as potentially affecting the very nature of the ability which is tested, and thus impact on validity as much as reliability. Replications and generalisability `A person with one watch knows what time it is; a person with two watches is never quite sure. Information from only one observation may easily deceive, because unverifiable, while to get direct information about consistency. Even more importantly, Brennan argues, `they are required for an unambiguous conceptualization of the very notion of reliability. The individual variation in test-takers from one day to another is difficult to measure, because the test is taken only once. Thus its impact is very likely ignored, leading to an overestimate of reliability, unless we can do specific experiments to replicate the testing event in a way that will provide evidence. Variable severity in markers will contribute undetected error unless steps are taken to control this by extra training, multiple marking or scaling. In a writing test one test version might set an imaginative task and another an argumentative essay. Whether these are seen as replications of the same test procedure depends on how the writing construct has been defined. Stating what would constitute a replication of a test forces the test designer to be absolutely specific about which facets are relevant. Reliability and dependability Dependability is a term sometimes used (in preference to reliability) to refer to the consistency of a classification that is, of a test-taker receiving the same grade or score interpretation on repeated testing. The way the term is used relates to the distinction made between norm-referenced and criterionreferenced approaches to testing (see the chapters by Davidson and by J. The term dependability is used in a criterion-referencing context where the aim is to classify learners, for example as masters or non-masters of a domain of knowledge. True, reliability is defined in terms of the consistency with which individuals are ranked relative to each other, but in many testing applications it is no less concerned with consistency of classification relative to cut-off points that have well-defined criterion interpretations. All approaches to testing may be concerned with dependability of classification, whatever the terms or the procedures used.
This explains why some monozygotic twins are wrongly stated to be dizygotic twins at birth hair loss cure xian generic 0.5 mg dutasteride with visa. Awareness of this possibility must be considered when discrepancies occur between prenatal cytogenetic findings and the karyotype of an infant hair loss 7 year old boy discount 0.5 mg dutasteride otc. These attached (Greek hair loss hiv generic dutasteride 0.5 mg line, pagos hair loss 6 months post partum dutasteride 0.5 mg otc, fixed) twins are named according to the regions that are attached. It has been estimated that the incidence of conjoined twins is 1 in 50,000 to 100,000 births. In some cases, the twins are connected to each other by skin only or by cutaneous and other tissues. Some conjoined twins can be successfully separated by surgical procedures (see. Such twins rarely survive because their umbilical cords are often so entangled that interruption of the blood supply to the fetuses occurs. Superfecundation Superfecundation is the fertilization of two or more oocytes at different times. In humans, the presence of two fetuses in the uterus caused by fertilization at different times (superfetation) is rare. Other Types of Multiple Births Triplets may be derived from: One zygote and be identical Two zygotes and consist of identical twins and a singleton Three zygotes and be of the same sex or of different sexes In the last case, the infants are no more similar than infants from three separate pregnancies. Similar combinations occur in quadruplets, quintuplets, sextuplets, and septuplets. The two parts are held together by stem chorionic villi that attach to the cytotrophoblastic shell surrounding the chorionic sac, which attaches the sac to the decidua basalis. The principal activities of the placenta are metabolism (synthesis of glycogen, cholesterol, and fatty acids), respiratory gas exchange (oxygen, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide), transfer of nutrients (vitamins, hormones, and antibodies; elimination of waste products), and endocrine secretion. It is a permeable membrane that allows water, oxygen, nutritive substances, hormones, and noxious agents to pass from the mother to the embryo or fetus. Excretory products pass through the placental membrane from the fetus to the mother. The fetal membranes and placenta(s) in multiple pregnancies vary considerably, depending on the derivation of the embryos and the time when division of embryonic cells occurs. Twins with one amnion, one chorion, and one placenta are always monozygotic, and their umbilical cords are often entangled. The umbilical vesicle and allantois are vestigial structures; however, their presence is essential to normal embryonic development. Both are early sites of blood formation and both are partly incorporated into the embryo. Primordial germ cells also originate in the wall of the umbilical vesicle (yolk sac). The amnion forms an amniotic sac for amniotic fluid and provides a covering for the umbilical cord. The amniotic fluid has three main functions: to provide a protective buffer for the embryo or fetus, to allow room for fetal movements, and to assist in the regulation of fetal body temperature. The arrows indicate the umbilical vesicles of the dizygotic twins in their chorionic sacs. B, Diamniotic/monochorionic twin gestation at 11 weeks, 9 weeks after fertilization. Note the two clavicles supporting the midline upper limb, fused thoracic cage, and parallel vertebral columns. Chorionic villus sampling and chromosome analysis revealed that the twins were likely female. An ultrasound examination of a pregnant woman during the second trimester revealed multiple amniotic bands associated with the fetus. Foidart J-M, Hustin J, Dubois M, Schaaps J-P: the human placenta becomes haemochorial at the 13th week of pregnancy. Pridjian G: Fetomaternal interactions: Placental physiology, the in utero environment, and fetal determinants of adult disease. Spencer R: Theoretical and analytical embryology of conjoined twins: Part I: Embryogenesis.
Buy dutasteride 0.5 mg cheap. RELAXED GIRL REACTS TO WHITE GIRL RELAXING HER HAIR & IT FALLS OUT.
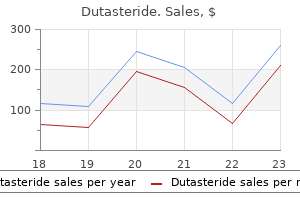
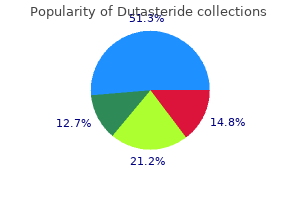
However hair loss nyc buy 0.5 mg dutasteride mastercard, in 25% of the population hair loss treatment using stem cells order 0.5 mg dutasteride with amex, it arises from the inferior epigastric or the external iliac artery hair loss in men zara dutasteride 0.5 mg low cost. There is considerable variation as to the origins of the branches of the posterior and anterior trunks of the internal iliac artery hair loss cream buy 0.5 mg dutasteride amex. The internal pudendal artery (answer a), umbilical artery (answer d), and uterine artery (answer e) almost always arise from the anterior trunk. Varicoceles are a stasis of blood within the pampiniform plexus and occur most frequently on the left side because the testicular vein on the left drains into the higher pressure left renal vein, whereas the right testicular vein drains into the inferior vena cava. A femoral hernia (answers c and d) would not end up in the scrotum, rather within the thigh. Cryptorchidism (answer a), that is an undescended testicle, on the right side does not fit the physical examination findings. Although the preganglionic fibers arise between T1 and L2, each of the sacral ganglia has a gray ramus that brings postganglionic fibers to the associated spinal nerve. These sympathetic neurons mediate sweating (sudomotor), vasoconstriction (vasomotor), and piloerection (pilomotor) in dermatomes S1S5. Male ejaculation is practically mediated by skeletal muscle (contraction of the bulbospongiosus muscle innervated by superficial perineal nerves, branches of the pudendal nerve. Emission (rapid contraction of the vas deferens) is mainly mediated by sympathetic, but mainly by lumbar splanchnic nerves, thereby bypassing the sympathetic chain ganglia. Erection in both male and female (answers c and d) is mainly mediated by parasympathetic nerves. Bladder contraction (answer a) is also mainly controlled by parasympathetic nerves. Contraction of the internal urethral sphincter is under control of the sympathetic nervous system [thus not (answer a)]. Concomitant with dilation of the helicine arteries under parasympathetic innervation [thus not (answers b and c)], which allows increased blood to flow into the cavernous spaces, contraction of the bulbospongiosus and ischiocavernosus muscles at the base of the cavernous Pelvis Answers 555 bodies reduce blood from leaving, resulting in engorgement and penile or clitoral erection. Emission of seminal fluid, prostatic secretions, and sperm from the vas deferens is due to contraction of smooth muscle under sympathetic control [thus not (answer d)]. These structures are seen bilaterally between the alae of the sacrum and the ilia. The pathway for spinal nerves (answer c) is through foramina of the sacrum, not through long bony canals. Similarly, the pathway for the gluteal arteries (answers d and e) is through the greater sciatic foramen between the ilium and the sacrum. The purpose of performing a hysterosalpingogram is to determine if the fallopian tubes are open and thus potentially capable of transporting sperm and eggs for conception. The dye is generally introduced via a catheter placed through the cervix and injected into the uterus. In this case it seems as if dye is spilling into the peritoneal cavity at ends of each fallopian tube. Within the image (E) is the vagina, (D) is the isthmus of the cervix, (B) is the body of the uterus, and A is the ampulla of the oviduct just proximal to the infundibulum out of which dye is flowing as curling wisps. The wall of the uterine cavity (answer b) is the normal site of implantation about 4 days later. Fertilization normally does not occur either in the infundibulum (answer c) nor isthmus of the oviduct (answer d). The suspensory ligament of the ovary runs from the pelvic brim to the lateral pole of the ovary. It contains the ovarian artery, ovarian vein, ovarian lymphatics, and ovarian nerves (ovarian neurovascular bundle). Volvulus of the ovary (usually associated with an ovarian tumor) may constrict the neurovascular bundle with ovarian infarct and pain referred to the inguinal and hypogastric regions. If the site of damage could be identified, then the duplicated left ureters could be connected above the damage to the undamaged ureter and may preserve full kidney function. While a pyelogram (answer a) does require injection of an iodine based dye that can cause some kidney damage, this should not cause damage specifically to the inferior half of the left kidney. The development of the kidney stone (answer d) within one of the left duplicated ureters would be unlikely, but if present then the stone should be evident on the pyelogram images.
Furthermore hair loss treatment video dutasteride 0.5 mg buy on line, after the sixth week hair loss due to stress buy dutasteride 0.5 mg fast delivery, dimensions of the head and trunk can be obtained and used for assessment of embryonic age hair loss cure - medicinal plants dutasteride 0.5 mg order with mastercard. There is hair loss cure vampire 0.5 mg dutasteride buy with amex, however, considerable variability in early embryonic growth and development. Differences are greatest before the end of the first 4 weeks of development, but less so by the end of the embryonic period. Figure 5-20 A, Lateral view of an embryo at Carnegie stage 23, approximately 56 days. C, A Carnegie stage 23 embryo, approximately 56 days after ovulation, imaged with optical microscopy (left) and magnetic resonance microscopy (right). The formation of the head, caudal eminence, and lateral folds is a continuous sequence of events that results in a constriction between the embryo and the umbilical vesicle (yolk sac). As the head folds ventrally, part of the endodermal layer is incorporated into the developing embryonic head region as the foregut. Folding of the head region also results in the oropharyngeal membrane and heart being carried ventrally, and the developing brain becoming the most cranial part of the embryo. As the caudal eminence folds ventrally, part of the endodermal germ layer is incorporated into the caudal end of the embryo as the hindgut. Folding of the caudal region also results in the cloacal membrane, allantois, and connecting stalk being carried to the ventral surface of the embryo. Folding of the embryo in the horizontal plane incorporates part of the endoderm into the embryo as the midgut. The umbilical vesicle remains attached to the midgut by a narrow omphaloenteric duct (yolk stalk). During folding of the embryo in the horizontal plane, the primordia of the lateral and ventral body walls are formed. As the amnion expands, it envelops the connecting stalk, omphaloenteric duct, and allantois, thereby forming an epithelial covering for the umbilical cord. The three germ layers differentiate into various tissues and organs so that by the end of the embryonic period, the beginnings of all the main organ systems have been established. The external appearance of the embryo is greatly affected by the formation of the brain, heart, liver, somites, limbs, ears, nose, and eyes. As these structures develop, the appearance of the embryo changes so that it has unquestionably human characteristics at the end of the eighth week. Because the beginnings of most essential external and internal structures are formed during the fourth to eighth weeks, this is the most critical period of development. Developmental disturbances during this period may give rise to major congenital anomalies of the embryo. A 28-year-old woman who has been a heavy cigarette smoker since her teens was informed that she was in the second month of pregnancy. Physicians usually discuss the critical period of development with their patients. A woman who had just become pregnant told her doctor that she had accidentally taken a sleeping pill given to her by a friend. Hardin J, Walston T: Models of morphogenesis: the mechanisms and mechanics of cell rearrangement. Nishimura H, Tanimura T, Semba R, Uwabe C: Normal development of early human embryos: Observation of 90 specimens at Carnegie stages 7 to 13. Shiota K: Development and intrauterine fate of normal and abnormal human conceptuses. Yamada S, Uwabe C, Nakatsu-Komatsu T, et al: Graphic and movie illustrations of human prenatal development and their application to embryological education based on the human embryo specimens in the Kyoto Collection. Development during the fetal period is primarily concerned with rapid body growth and differentiation of tissues, organs, and systems. A notable change occurring during the fetal period is the relative slowdown in the growth of the head compared with the rest of the body. Periods of normal continuous growth alternate with prolonged intervals of absent growth. Viability of Fetuses Viability is defined as the ability of fetuses to survive in the extrauterine environment.
References
- Mehndiratta MM, Hughes RA. Corticosteroids for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculopathy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2002;(1):CD002062.
- Franko A, Dodic-Fikfak M, Arneric N, Dolzan V. Glutathione S-transferases GSTMA and GSTT1 polymorphisms and asbestosis. J Occup Environ Med 2007;49:667-71.
- Nagawa H, Muto T, Sunouchi K, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of lateral node dissection vs. nerve-preserving resection in patients with rectal cancer after preoperative radiotherapy. Dis Colon Rectum 2001;44(9):1274-80.
- Nijhawan D, Zack TI, Ren Y, et al. Cancer vulnerabilities unveiled by genomic loss. Cell 2012;150(4):842-854.