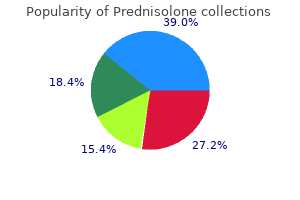
Prednisolone
Angelo Cuzalina, MD, DDS
- Private Practice - Tulsa Surgical Arts
- President, American Academy of Cosmetic Surgery 2011
- Chairman, AACS Cosmetic Surgery Fellowship Program
- Adjunct Clinical Assistant Professor of Surgery, Oklahoma
- State University
- Tulsa, Oklahoma
Scandinavia and Germany also rely on voluntary vaccination rather than compulsion allergy medicine 2015 generic prednisolone 5 mg. There are some vaccination requirements in Australia allergy symptoms fever discount prednisolone 40 mg fast delivery, but there is a broad right of conscientious objection food allergy symptoms 7 month old generic prednisolone 40 mg free shipping. Some provinces in Canada require vaccines but allow conscientious objection allergy ultratab effective 20 mg prednisolone, and the country as a whole does not mandate vaccination. While there are other vaccination mandates in the United States for military personnel, hospital workers, and university students, to name a few, this Article focuses exclusively on state mandates for preschoolers and schoolchildren. Today, if children do not comply with state vaccination mandates and do not have valid exemptions, they lose their ability to attend school, a fundamental right and obligation of 12 citizenship. Further, state agents may charge the parents with medical neglect and potentially remove children to foster care for 13 failure to vaccinate. Even if a state offers limited medical, religious, and philosophical exemptions, we consider its vaccination mandate to be compulsory for purposes of this Article. We do so because in the 14 majority of states, exemptions are extremely limited, and even in those states where they exist, there are strong legislative efforts to 15 curtail them. We note at the outset that many vaccine-related issues are beyond the scope of this Article. While further considerations of population of roughly 63 million, had 0 reported cases of diphtheria, 2092 reported cases of measles, and 3178 reported cases of mumps. Similarly, Australia, with a population of roughly 23 million, had 0 reported cases of diphtheria, 199 reported cases of measles, and 195 reported cases of mumps in 2012. In 2012, the United States, where choice is more limited, with a population of roughly 317 million, had 1 reported case of diphtheria, 55 reported cases of measles, and 229 reported cases of mumps. Part I defines and analyzes herd immunity and the closely related but distinct concept of herd effect. It contrasts disease eradication and elimination with control, highlighting the limits of what modern vaccination programs can achieve. It then explores the real world of disease outbreaks in vaccinated and unvaccinated populations. This systematic approach highlights seven objectives of vaccination programs, including mandatory ones. In a population of only susceptible individuals, the introduction of a single infected person will result in indiscriminate transmission to all others whom the infected person contacts until those infected people die or 18 recover. The average number of people in such a susceptible population who become infected is the so-called basic reproduction 19 number R0. Each of those people who contracted the disease from the initial infected individual is able to transmit the disease to other susceptible contacts; this process repeats itself until the entire 16 Other sources provide more in-depth considerations of these issues. Herd Immunity Threshold By contrast, consider the case where a certain fraction of the population has immunity to the disease. If a single infected individual comes into the population, the average number of secondary 22 infections from transmission is then R0(1- ). If R0(1- ) < 1, then the 23 disease on average will not spread to other susceptible people. The threshold H of immune individuals to create these circumstances is H = 1-1/R0, or 25 the herd immunity threshold. The underlying rationale for mass vaccination policies is to ensure that the fraction of immune individuals in society is above the herd immunity threshold, thus 26 eliminating the disease from the population. The moral of the herd immunity story, though, is that not every individual needs to be 27 immune to provide protection to the society as a whole. Even if herd immunity itself is not achievable, society still benefits from a "buffer" of immune individuals in order to 30 mitigate disease. Although the concepts of herd immunity and herd effect are sometimes interchangeable, they describe different aspects of the immunity puzzle-whereas herd immunity aims to eliminate a 31 disease from society, herd effect refers to infection control. Since the 1960s, compulsory state vaccination programs have achieved herd effects for specific diseases, but none has achieved herd immunity. The Free Rider Problem Why are universal mandatory vaccination policies necessary if we can achieve herd immunity by vaccinating only a fraction of the population?
Overall allergy shots brand names order 40 mg prednisolone otc, the data obtained may be interpreted as initial radiation exposure bringing forward in time the natural process of clonal telomeric sequence instability associated with cell senescence and telomere shortening juniper allergy treatment buy prednisolone 10 mg low cost. A different form of postirradiation telomere-associated instability is expressed in a hamster-human hybrid cell system (Marder and Morgan 1993) where allergy symptoms with dizziness prednisolone 10 mg order on line, in some clones allergy shots child best prednisolone 40 mg, chromosomal instability is persistently expressed at translocations that have telomeric sequences at their junction (Day and others 1998). Similarly, unstable structures have been observed in unirradiated hamster cells undergoing gene amplification (Bertoni and others 1994), and again it may be that radiation is inducing genomic structures that enhance the natural expression of instability. There is good evidence that telomeric sequence instability is a recurrent feature of tumorigenic development (Bacchetti 1996; Chang and others 2001; Murnane and Sabatier 2004). Of particular relevance to the question of unstable translocation junctions are the so-called segmental jumping translocations that have been well characterized in spontaneously arising human leukemias (Shippey and others 1990). In respect of radiation tumorigenesis, detailed cytogenetic analyses suggest an excess of complex aberrations and segmental jumping translocations in myeloid leukemias arising at old ages in high-dose-exposed atomic bomb survivors (Nakanishi and others 1999). These and other data on excess microsatellite instability in A-bomb myeloid leukemias (Nakanishi and others 2001) have been reanalyzed in respect of dose and probability of tumor causation (Cox and Edwards 2002; Little 2002). These reanalyses largely uncouple the expression of leukemia-associated jumping translocations and microsatellite instability from radiation causation and argue that the potential contribution of induced instability to leukemogenic risk is likely to be small. In conclusion, although the position regarding radiationinduced persistent genomic instability and its causal association with tumorigenesis is not well understood, a few specific points can be made: 1. In the case of radiation-associated persistent telomeric rearrangement and unstable chromosome translocation junctions, a coherent case can be made that a certain fraction of misrepaired genomic damage after radiation may be prone to ongoing secondary change in clonal progeny. There is evidence that such secondary genomic rearrangement can be a normal component of tumor development, in which case it is reasonable to assume that excess instability of this type could be a feature of some radiation-associated tumors, particularly those arising after high-dose irradiation where multiple or complex rearrangements may be expected. The genetic evidence from mouse studies that postirradiation chromatid instability can be associated with mammary tumor development is also persuasive, although it leaves unanswered questions on the causal role of the excess chromatid damage observed in vitro. Based on the negative or inconsistent data on in vivo induced genomic instability in bone marrow cells, the nonsharing of genetic determinants, and the contention on data regarding A-bomb leukemias, induced genomic instability is judged unlikely to impact appreciably on the risk of lymphohematopoietic tumors after low-dose radiation. There are very few data on radiation-associated human solid tumors from which to assess the potential contribution of induced genomic instability. The central problem is the inherent difficulty in distinguishing this specific radiationinduced phenotype from spontaneously developing genomic instability as a natural consequence of clonal selection during tumor development. Stated simply, does tumor instability correlate with initial radiation damage or with neoplastic phenotype? This problem is well evidenced by molecular studies on post-Chernobyl (Belarus) childhood thyroid cancer. Initial studies showed evidence of excess microsatellite alterations in these radiation-associated tumors when compared with a reference group of adult thyroid cancers (Richter and others 1999). However, more detailed follow-up studies showed that the principal correlation was between microsatellite alterations and the aggression of early arising tumors. When this factor was taken into account, microsatellite loss or mutation in the early Belarus tumors was shown to be similar to that of the adult reference cases (Lohrer and others 2001). First, the adequacy of a study with respect to statistical power and use of appropriate analytical methodology must be considered. Second, biological factors involved in the pathogenesis of specific neoplasms must be considered with respect to the applicability of the experimental model to carcinogenesis in general and to cancer risk in humans in particular. Given these caveats, there are relatively few studies on animal carcinogenesis where the data are sufficient to address the issue of dose-response relationships or the issue of doserate effects and/or fractionation effects. Those studies in which such analyses are possible are limited mainly to rodent studies, principally mice. As discussed later in this chapter genetic background has a major role in determining neoplastic development at the level of sensitivity to both initiating events and events involved in expression. Therefore even in mouse studies in which there is sufficient statistical power to address questions of low-dose effects and time-dose relationships, the data are limited to mouse strains that are highly susceptible to specific forms of neoplasias. While variations in susceptibility must be considered potential confounding factors in applying animal data to human risks, careful analyses of human and animal data suggest that animal data do in fact have predictive value-for example, they can guide judgments on the choice of cancer risk models (Carnes and others 1998; Storer and others 1988). On the other hand, there are specific murine neoplasms whose pathogenesis appears to be unique to the mouse. In these specific instances it is unlikely that data derived using these systems would be applicable to human risks. Specific Murine Neoplasms Based on consideration of the available in vivo data it is concluded that, at present, only a weak scientific case can be made for a discernible impact of induced genomic instability on radiation cancer risk.
The committee further judges it unlikely that a threshold exists for the induction of cancers but notes that the occurrence of radiation-induced cancers at low doses will be small allergy treatment dogs buy 10 mg prednisolone visa. The committee maintains that other health effects (such as heart disease and stroke) occur at high radiation doses allergy treatment options mayo clinic cheap prednisolone 5 mg buy, but additional data must be gathered before an assessment can be made of any possible connection between low doses of radiation and noncancer health effects allergy symptoms to kiwi fruit discount prednisolone 5 mg with mastercard. Additionally allergy testing on 6 year old generic prednisolone 20 mg with amex, the committee concludes that although adverse health effects in children of exposed parents (attributable to radiation-induced mutations) have not been found, there are extensive data on radiation-induced transmissible mutations in mice and other organisms. Thus, there is no reason to believe that humans would be immune to this sort of harm. Risk of radiation-induced cancer at low doses and low dose rates for radiation protection purposes. Ionizing radiation arises from both natural and man-made sources and at very high doses can produce damaging effects in tissues that can be evident within days after exposure. At the low-dose exposures that are the focus of this report, socalled late effects, such as cancer, are produced many years after the initial exposure. Additionally, effects that may occur as a result of chronic exposures over months to a lifetime at dose rates below 0. Medium doses are defined as doses in excess of 100 mGy up to 1 Gy, and high doses encompass doses of 1 Gy or more, including the very high total doses used in radiotherapy (of the order of 20 to 60 Gy). Well-demonstrated late effects of radiation exposure include the induction of cancer and some degenerative diseases. This process does not appear to differ from that which applies to spontaneous cancer or to cancers associated with exposure to other carcinogens. Animal data support the view that low-dose radiation acts principally on the early stages of tumorigenesis (initiation). Although data are limited, the loss of specific genes whose absence might result in animal tumor initiation has been demonstrated in irradiated animals and cells. Adaptation, low-dose hypersensitivity, bystander effect, hormesis, and genomic instability are based mainly on phenomenological data with little mechanistic information. The data suggest enhancement or reduction in radiation effects and in some cases appear to be restricted to special experimental circumstances. Although less well established, the available data point toward a single-cell (monoclonal) origin of induced tumors. These data also provide some evidence on candidate radiation-associated mutations in tumors. Certain point mutations and gene amplifications have also been characterized in radiation-associated tumors, but their origins and status are uncertain. Molecular and cytogenetic studies of radiation-associated animal cancers Copyright National Academy of Sciences. The cellular data reviewed in this report identified uncertainties and some inconsistencies in the expression of this multifaceted phenomenon. However, telomereassociated mechanisms1 did provide a coherent explanation for some in vitro manifestations of induced genomic instability. The data did not reveal consistent evidence for the involvement of induced genomic instability in radiation tumorigenesis, although telomere-associated processes may account for some tumorigenic phenotypes. However, the induction or development of these two cancer types is believed to proceed via atypical mechanisms involving cell killing; therefore it was judged that the threshold-like responses observed should not be generalized. Adaptive responses for radiation tumorigenesis have been investigated in quantitative animal studies, and recent information is suggestive of adaptive processes that increase tumor latency but do not affect lifetime risk. The review of cellular, animal, and epidemiologic or clinical studies of the role of genetic factors in radiation tumorigenesis suggest that many of the known, strongly expressing, cancer-prone human genetic disorders are likely to show an elevated risk of radiation-induced cancer, probably with a high degree of organ specificity. Cellular and animal studies suggest that the molecular mechanisms that underlie these genetically determined radiation effects largely mirror those that apply to spontaneous tumorigenesis and are consistent with the knowledge of somatic mechanisms of tumorigenesis. A major theme developing in the study of cancer genetics is the interaction and potential impact of more weakly expressing variant cancer genes that may be relatively common in human populations. Knowledge of such gene-gene and gene-environment interactions, although at an early stage, is developing rapidly. Given that the functional gene polymorphisms associated with cancer risk may be relatively common, the potential for significant distortion of population-based risk was explored with emphasis on the organ specificity of genes of interest. The risk estimates presented in this report incorporate all of the above advances. The total risk for all classes of genetic diseases estimated in this report is about 3000 to 4700 cases per million firstgeneration progeny per gray.
Syndromes
- Mononucleosis
- Have a white or yellow center (contain pus)
- Vomiting, possibly bloody
- Oral thrush ("yeast infection")
- A child who has been vomiting for more than 12 hours (in a newborn under 3 months you should call as soon as vomiting or diarrhea begins)
- Able to feed self neatly, with minimal spilling
The nodule should be removed with monopolar hook or cold scissor trying to be radical on the disease and conservative toward the function minimizing the risk of postoperative complications allergy forecast today austin tx cheap prednisolone 10 mg online. Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this activity allergy medicine otc best best prednisolone 5 mg, the participant will be able to: 1) Describe how to approach posterior compartment endometriosis; 2) Discuss the different surgical technique to approach bowel endometriosis; and 3) Perform a deep endo bowel shaving procedure allergy symptoms mold spores trusted prednisolone 20 mg. Laparoscopic Excision of Deep n ltrating Endometriosis with Bowel and Parametrial Involvement plus Live Preoperative Ultrasound Surgeon: Mario Malzoni Rome allergy testing zones generic prednisolone 10 mg buy, Italy Moderators: Rosanne M. Diamond, Augusta, Georgia Case #1: Uterine septum is the most common congenital malformation reported in clinical practice. Hysteroscopic management is recognized as the gold standard for the management of this frequently encountered pathology. The following unedited video will illustrate a step-by-step approach to the hysteroscopic management of a septate uterus. Intrauterine landmarks which must be recognized to ensure safety and successful outcomes will be highlighted. Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: 1) Describe a step-by-step Nucelio Lemos Toronto, Ontario, Canada Moderators: Sven Becker, Frankfurt, Germany, M. Jonathon Solnik, Toronto, Ontario, Canada this case provides a live surgical demonstration of laparoscopic surgery in a setting of advanced pelvic endometriosis with previous live ultrasound. This is an effective technique in symptomatic patients when medical options fail or are poorly tolerated/ contraindicated. It can be considered a feasible and safe procedure, but a highly complex surgery, requiring specific skills in laparoscopic procedures with dedicated preoperative evaluation and optimal knowledge of surgical anatomy (neuro anatomy) and the handling of instruments and electrosurgery technologies. This session demonstrates surgical technique, discusses appropriate candidates for this procedure, and shows tips and tric s to overcome the di culties related to distortion of pelvic anatomy due to severe pelvic deep infiltrating endometriosis. Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: 1) Perform key points of pelvic Autonomic nerve damage is one of the most important causes of morbidity after radical resection of endometriosis. Techniques for surgical handling of pelvic nerves will be discussed and demonstrated, as well as the concept of nerve-sparing surgery through the direct visualization of nerve bundles. Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: 1) Recognize the autonomic and somatic nerve bundles crossing the pelvis; 2) discuss which steps of radical resection of endometriosis are most associated to autonomic nerve damage; and 3) implement essential nervesparing techniques into their practice. T-shaped uterus is characterized by a narrow uterine cavity due to thickened lateral walls with a correlation 2/3 uterine corpus and 1/3 cervix. This unedited video of a hysteroscopic enlargement metroplasty of a T-shaped uterus with fundal indentation using a 15 F miniresectoscope. The cardinal steps of the procedure are carefully explained to illustrate the procedure. Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: 1) Illustrate a simple Shailesh P. Laparoscopic retrieval of the uterus from a donor provides longer pedicle lengths; better ligation of branches of the uterine artery; shorter surgical time and lesser morbidities for donor surgery. The patient benefits with improved vascular anastomoses, in turn, reducing chances of rejection. Laparoscopic retrieval helps in better visualization, and replicable steps to all young aspirants. Learning Objective: At the conclusion of this activity, the participant will be able to: 1) Demonstrate and discuss the Errico Zupi Siena, Italy Moderators: Andrew I. W E D N E S D A Y this course provides a global overview on how to approach posterior compartment endometriosis that can be applied on every case to identify the anatomical structures that must be preserved during this kind of procedure. The video shows a simple procedures for uterus transplantation and general issues. The times listed are the times at which the author will present the poster, however, the poster can be viewed at any time. Burnett 9:50 Station P 1138 - Repeat Laparoscopy for Pregnancy of Unknown Location A. Eisenstein 9:50 Station C 2526 - Utilizing Quality and Value Metrics to Improve Patient Outcomes Through the Kaiser Permanente Minimally Invasive Hysterectomy Initiative M. Zaritsky 9:50 Station D 15 - the cacy and Safety of ong-Term Management of Uterine Fibroids with Ulipristal Acetate H.
Generic prednisolone 40 mg visa. Grains - Symptoms of Gluten Intolerance.
References
- Vestergaard K, Andersen G, Gottrup H, Kristensen BT, Jensen TS. Lamotrigine for central poststroke pain: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology 2001;56:184-190.
- Hirschmann JV, Raugi GJ: Blue (or purple) toe syndrome, J Am Acad Dermatol 60:1-20, 2009 quiz 21-22.
- Orlow I, LaRue H, Osman I, et al: Deletions of the INK4A gene in superficial bladder tumors. Association with recurrence, Am J Pathol 155:105n113, 1999.
- Schaner EG, Barlow JE, Doppman JL: Computed tomography in the diagnosis of subcapsular and perirenal hematoma. AJR 1977; 129:83-88.
- Gracely RH, Dubner R, McGrath PA. Narcotic analgesia: fentanyl reduces the intensity but not the unpleasantness of painful tooth pulp sensations. Science. 1979;203:1261-1263.
- Margreiter R, Klemp-auer J, -euhaus P, et al. Alemtuzumab (Campath-1H) a-d tacrolimus mo-otherapy after re-al tra-spla-tatio-: results of a prospective ra-domized trial. Am J Tra-spla-t. 2008;8(7):1480-1485.
- Bartek J, Lukas J, Bartkova J: Perspective: defects in cell cycle control and cancer, J Pathol 187:95n99, 1999.